When there’s swelling and restriction in your knee, it’s an indication that fluid has built up in the knee joint. This is most often due to effusion of the knee joint, usually caused by injuries like a torn ligament or dislocated kneecap. There are plenty of other issues that can cause this swelling, but if appropriately treated, the knee can make a full recovery.
What Is An Effusion In The Knee, And Why Does It Happen?
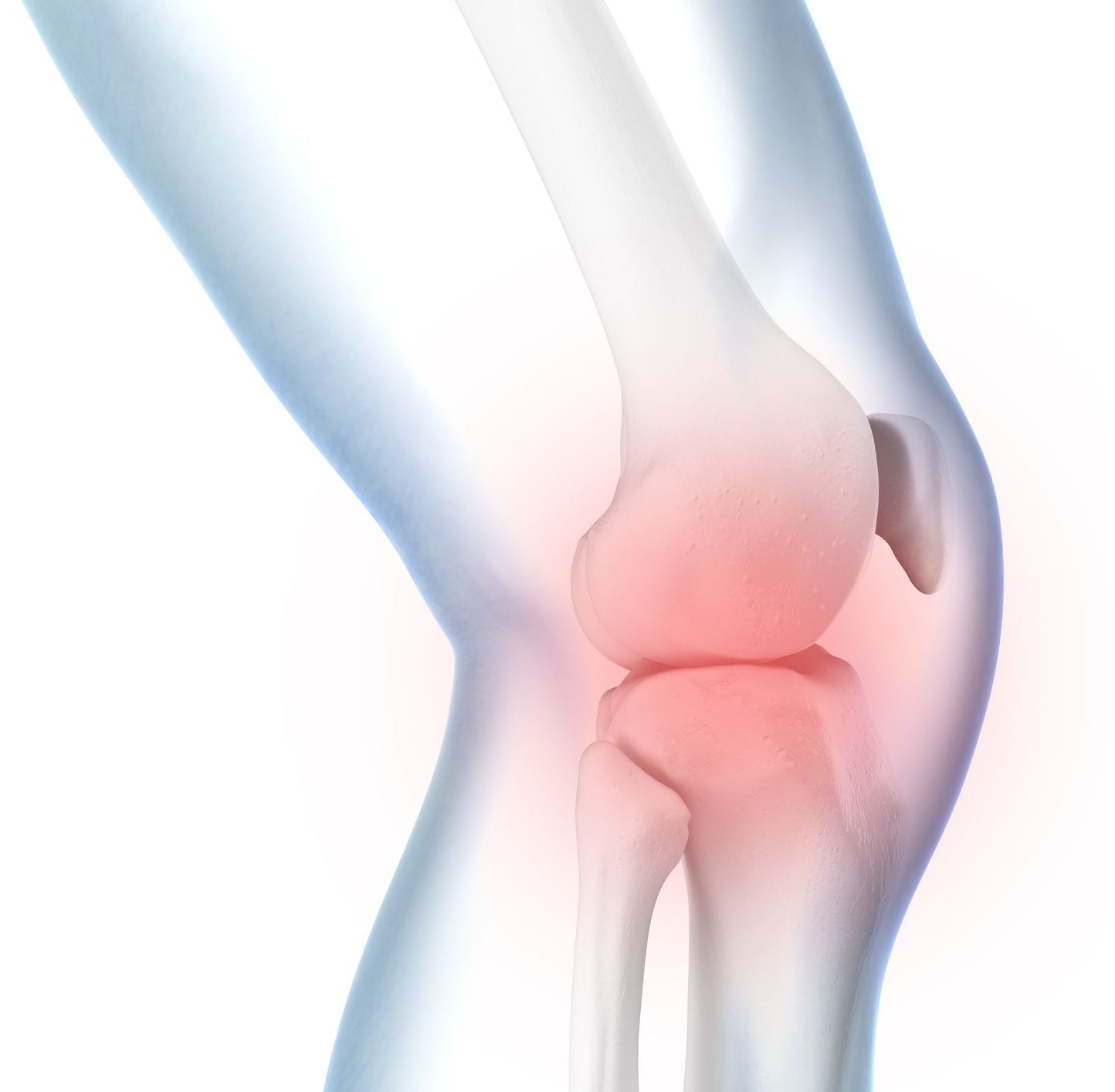
In the case of knee joint effusion, a noticeable amount of fluid builds up in knee capsule, which is often excess joint fluid, blood or pus. Your doctor will differentiate between an acute or chronic effusion based on the following:

- An acute infection is triggered by bacteria or viruses (e.g. post-op infection)
- Chronic inflammation can originate from injuries or damage to the surrounding area from overuse.
- Chronic inflammation without traumatic causes is caused most often by autoimmune diseases
Other possible causes are rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and other degenerative conditions, especially in more elderly people.
Symptoms Of A Knee Joint Effusion
Swelling is the first sign of joint effusion, with restricted movement and pain inside the joint, particularly behind the kneecap, following. If the knee is red and hot to the touch, that’s a strong indicator there’s an infection as well.
How Is Joint Effusion Diagnosed?
A doctor can perform several tests to check for joint effusion in the knee, including
- Patella test, which involves moving the patella and checking for how it reacts.
- Bursa test, where the bursa is moved above the kneecap to look for protrustions around the knee.
- Imaging tools like ultrasound, X-rays and MRI all work well.
Treatment Options For A Joint Effusion In The Knee
If the knee issue is caused by a sports injury or a physical accident, first aid is the best chance at alleviating the issue quickly. Follow the RICE principle to stabilize the joint with the following steps:
- Rest the knee by avoiding physical activity.
- Ice the area on and off for 20 minutes after injury.
- Compress with bandages or a compression support.
- Elevate the leg to allow gravity to push the fluids out of the knee.
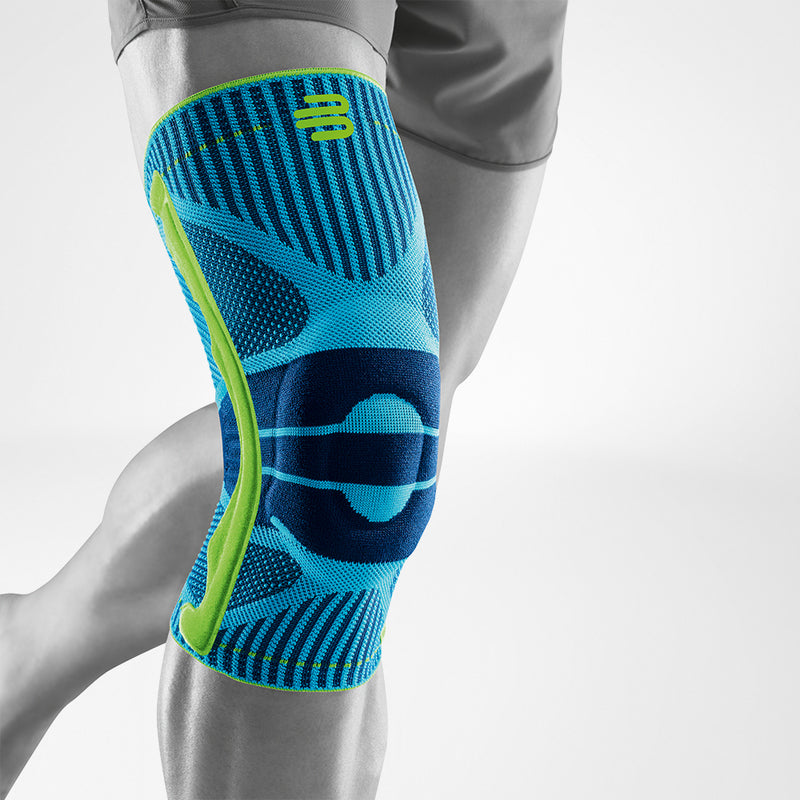
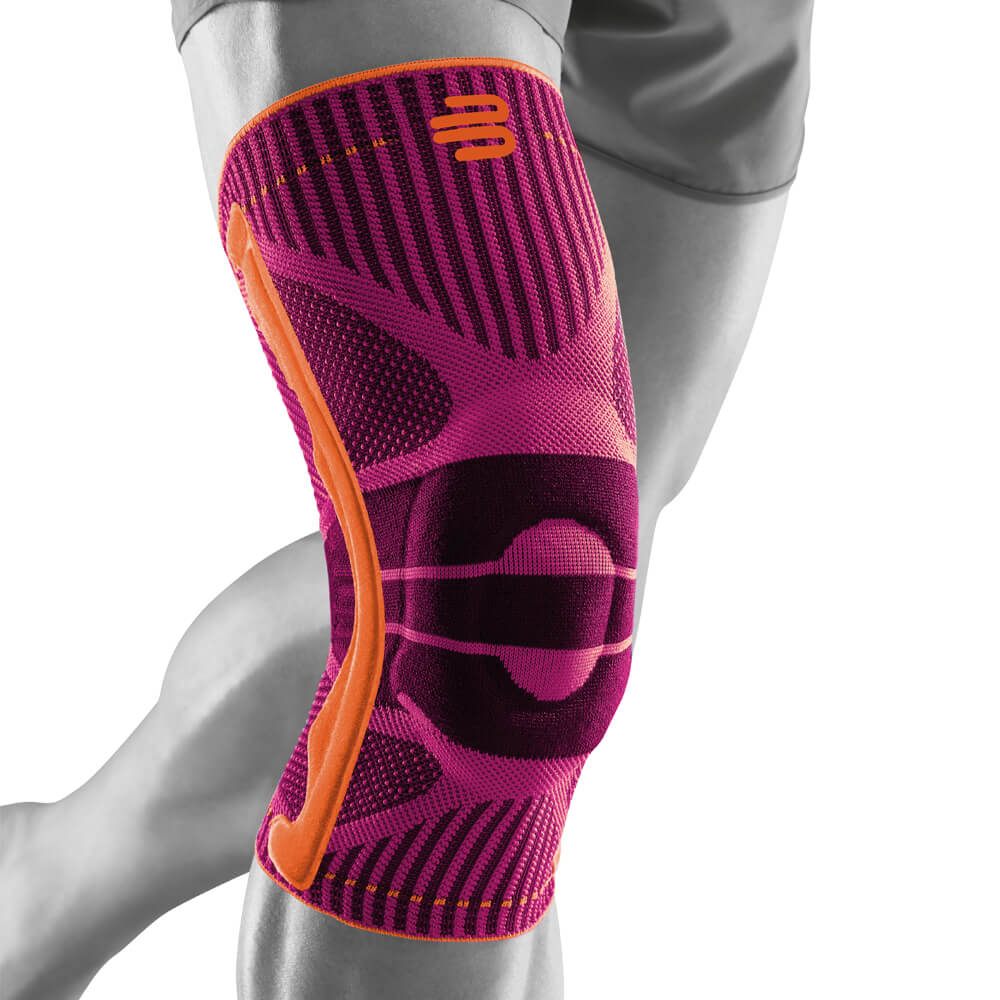
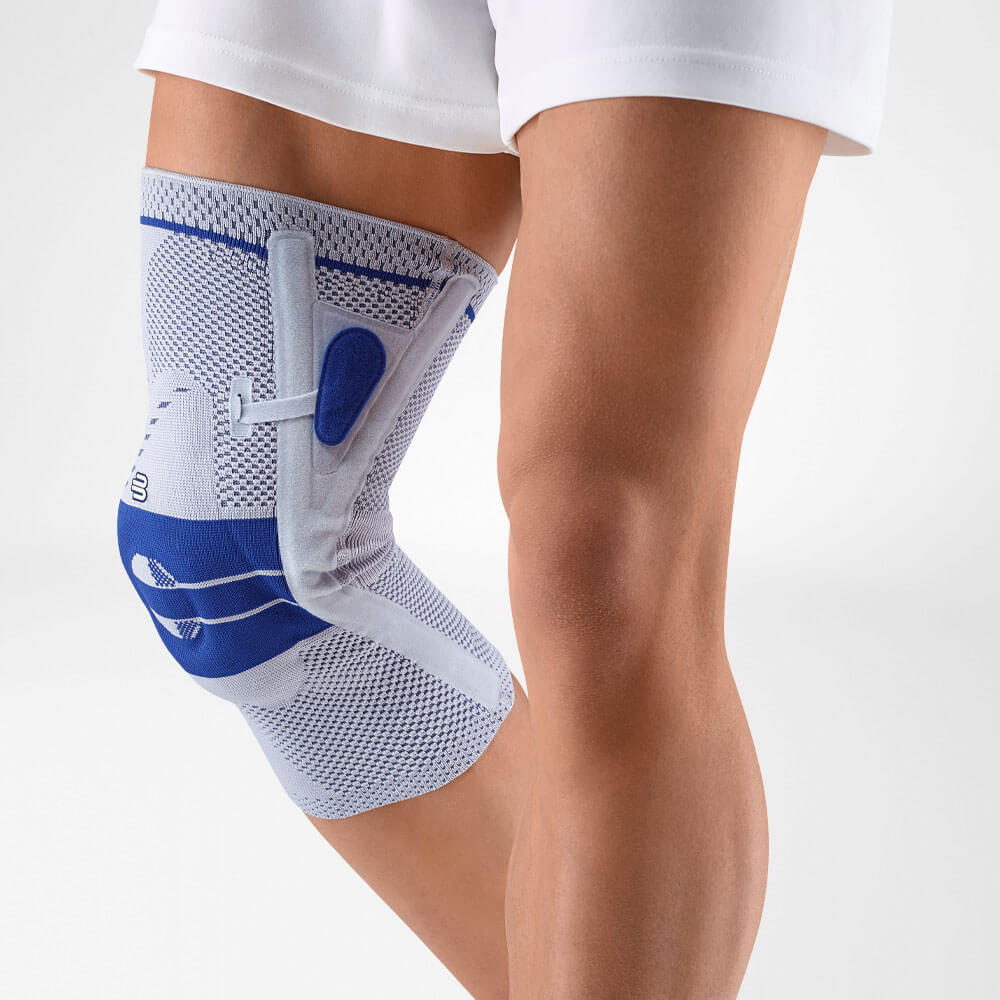
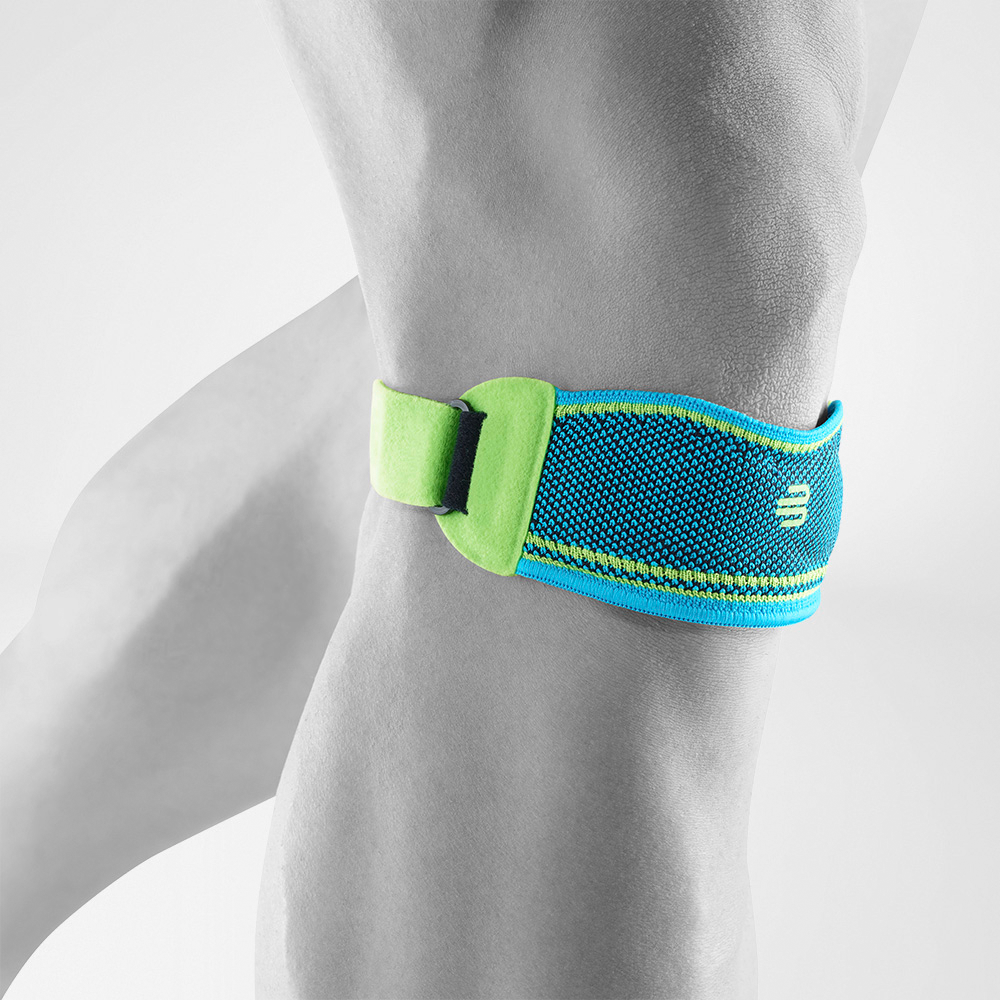
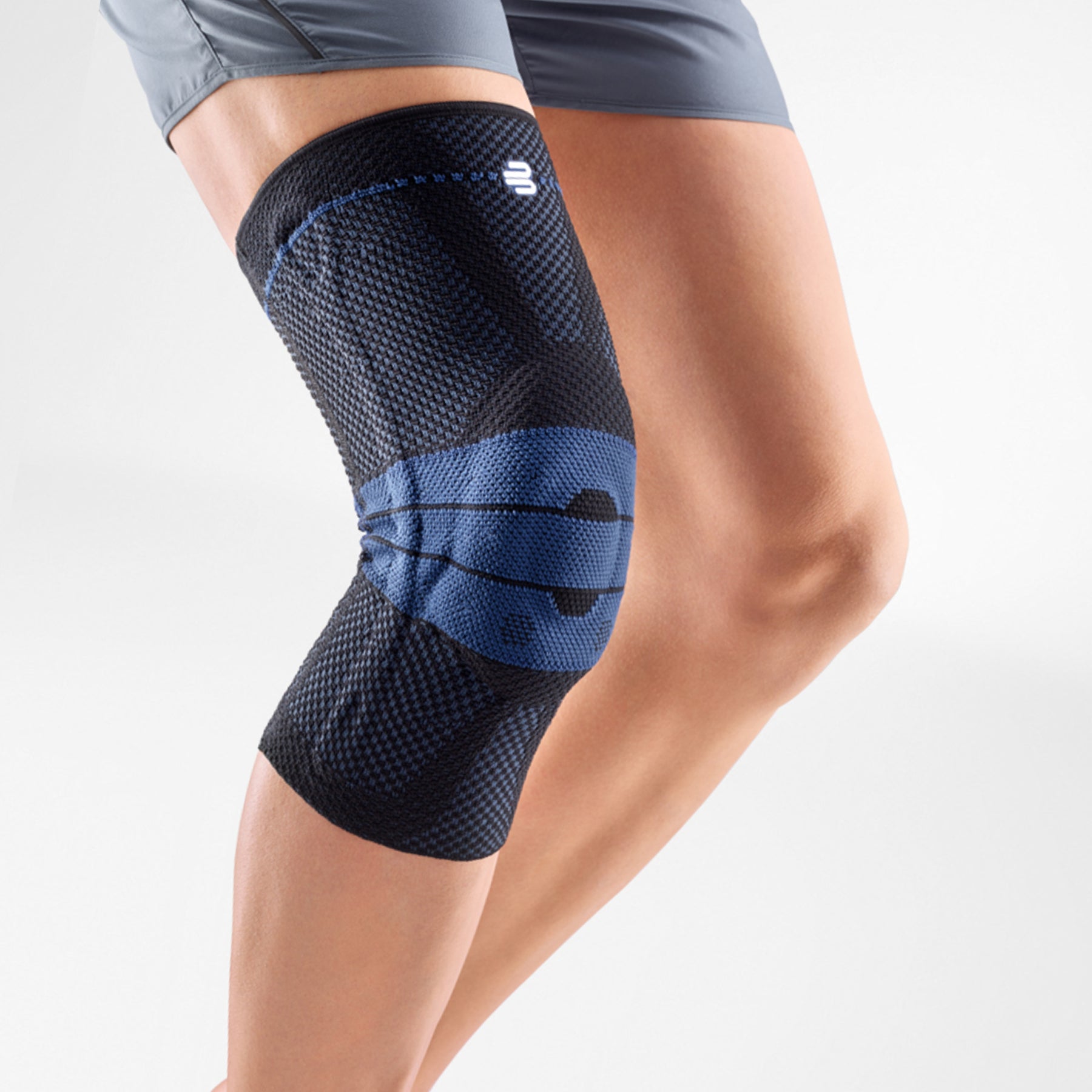
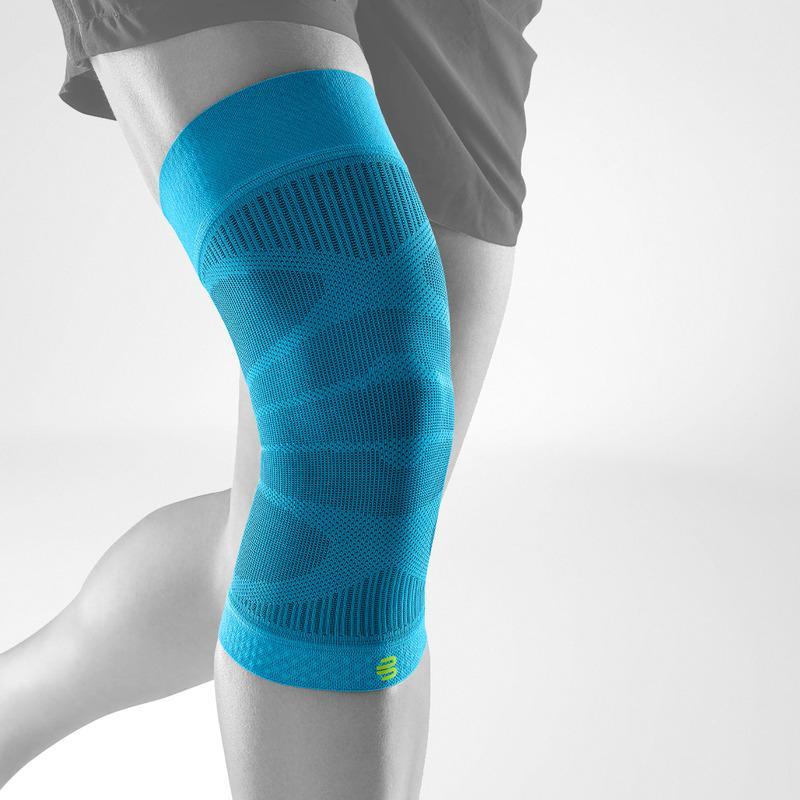
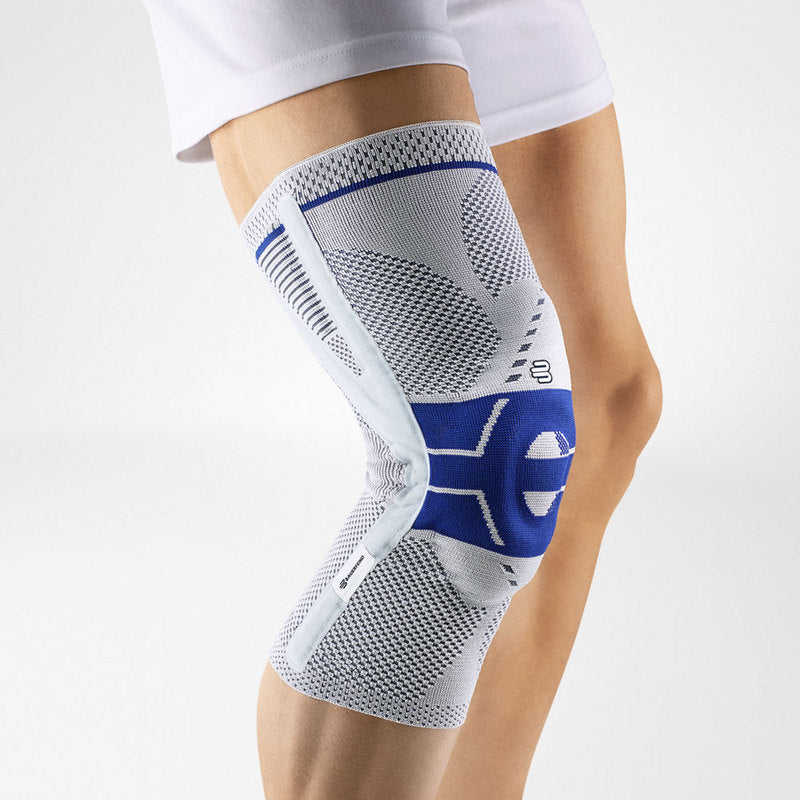
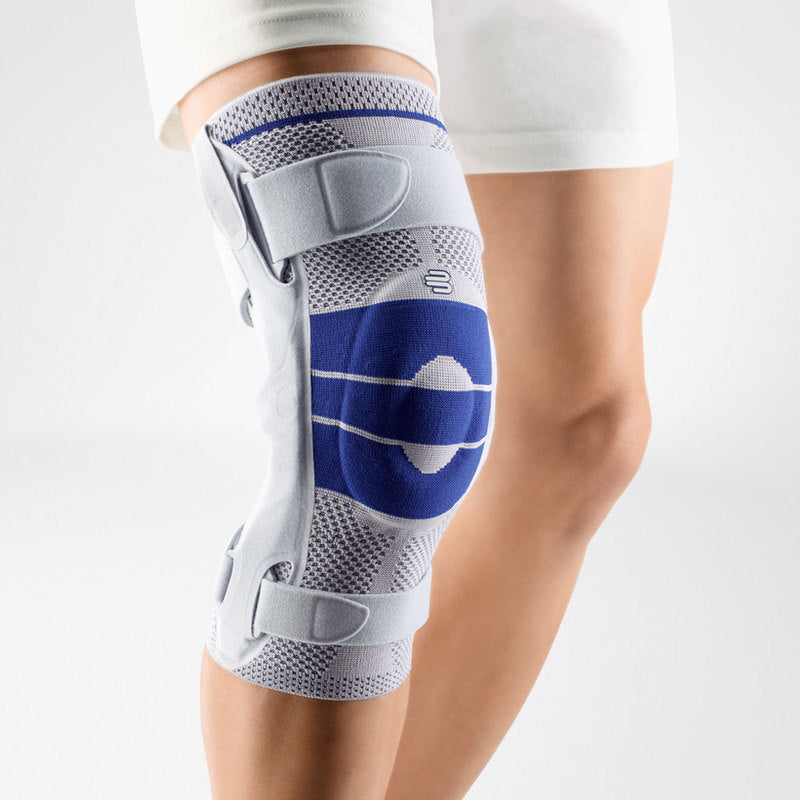
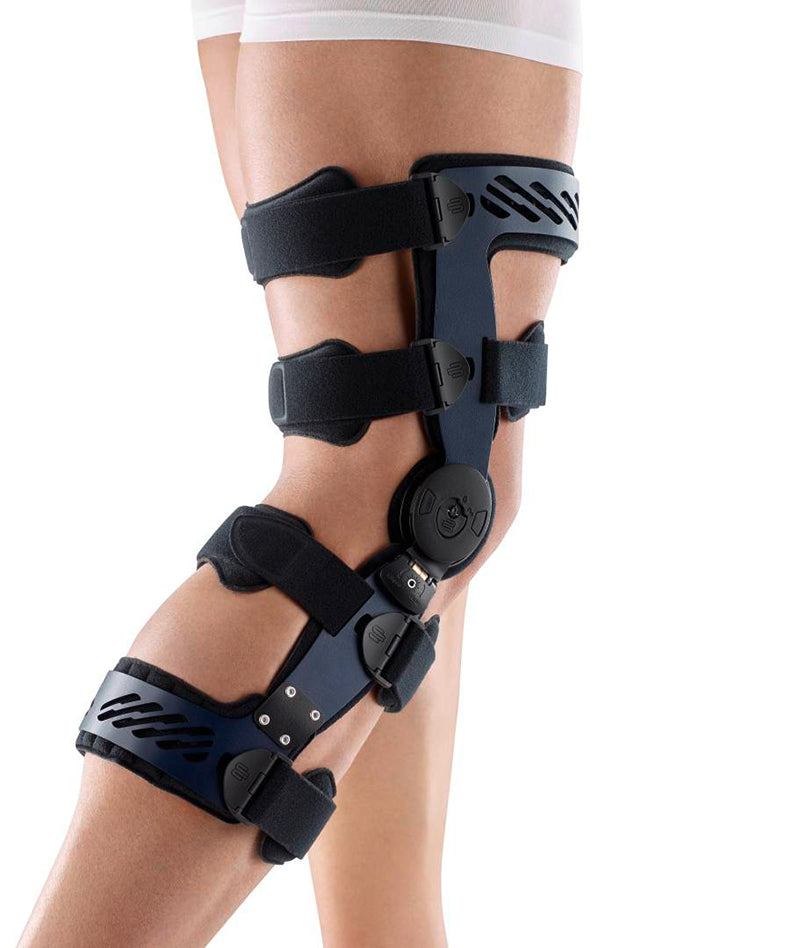
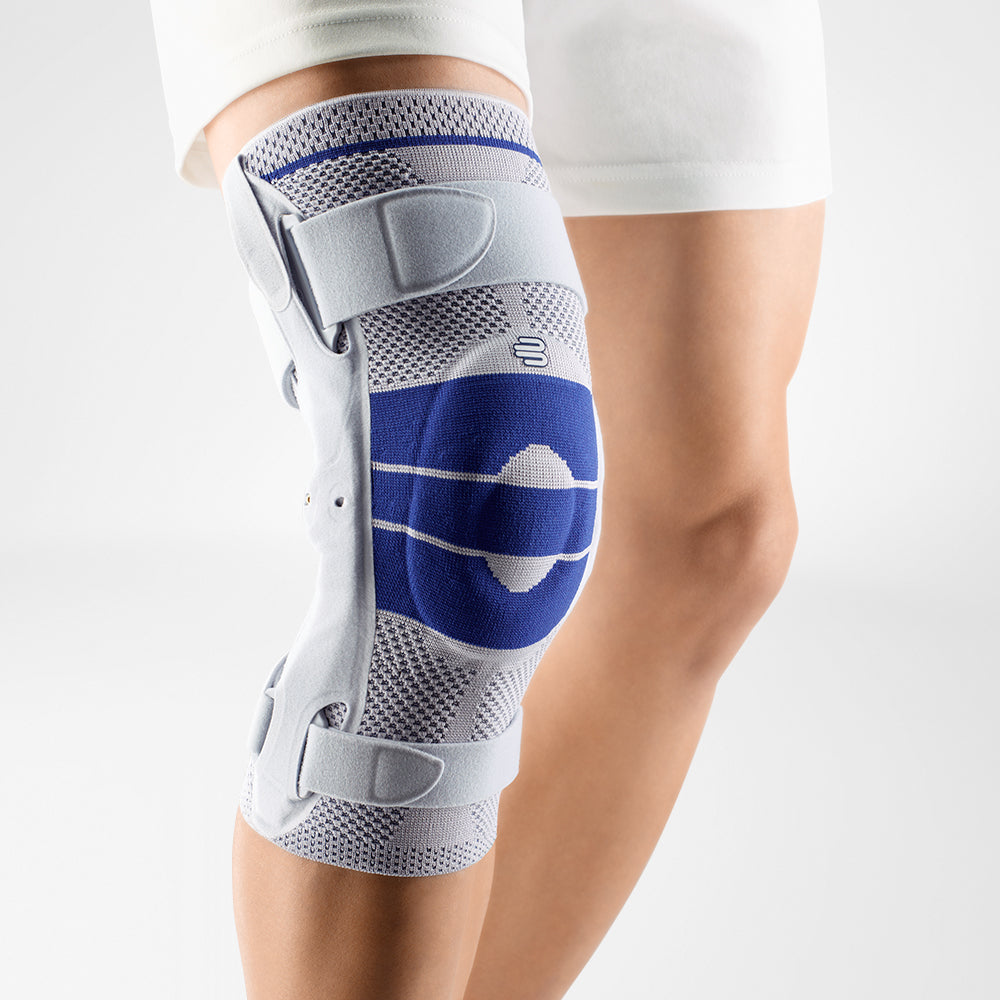
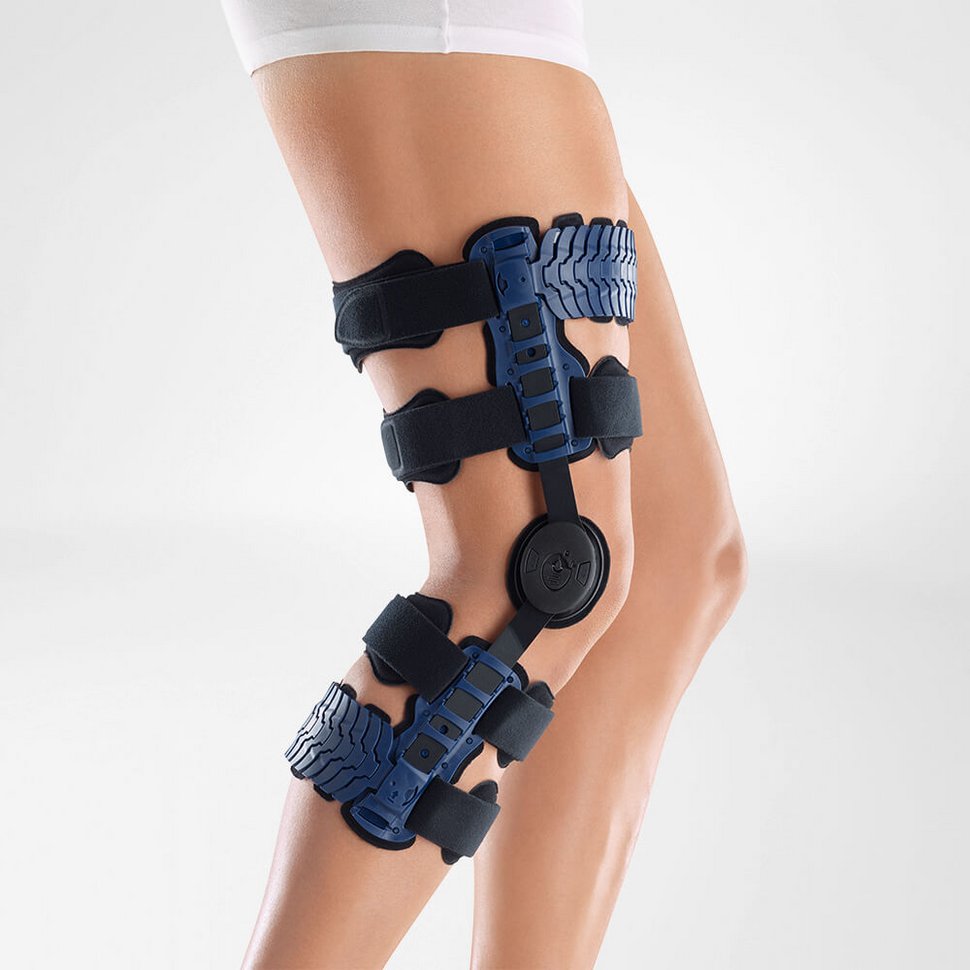
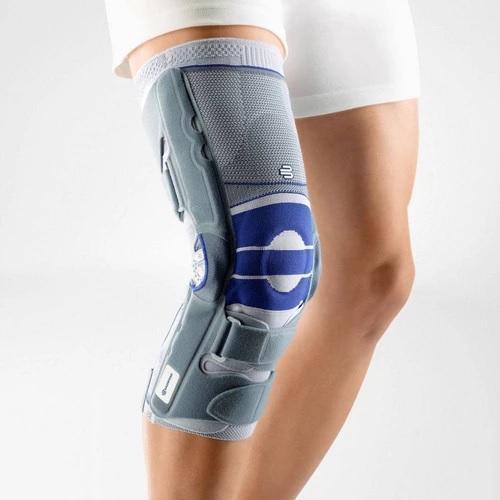
Effectively Support The Reduction Of The Knee Joint Effusion
While elevation and compression can help, there is a limit to their effectiveness, and this

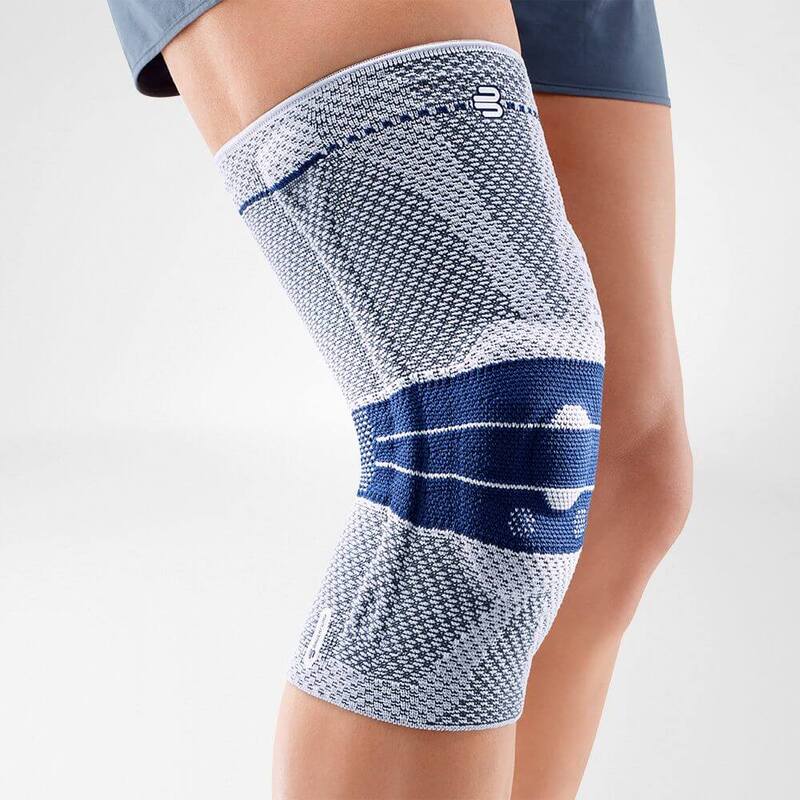
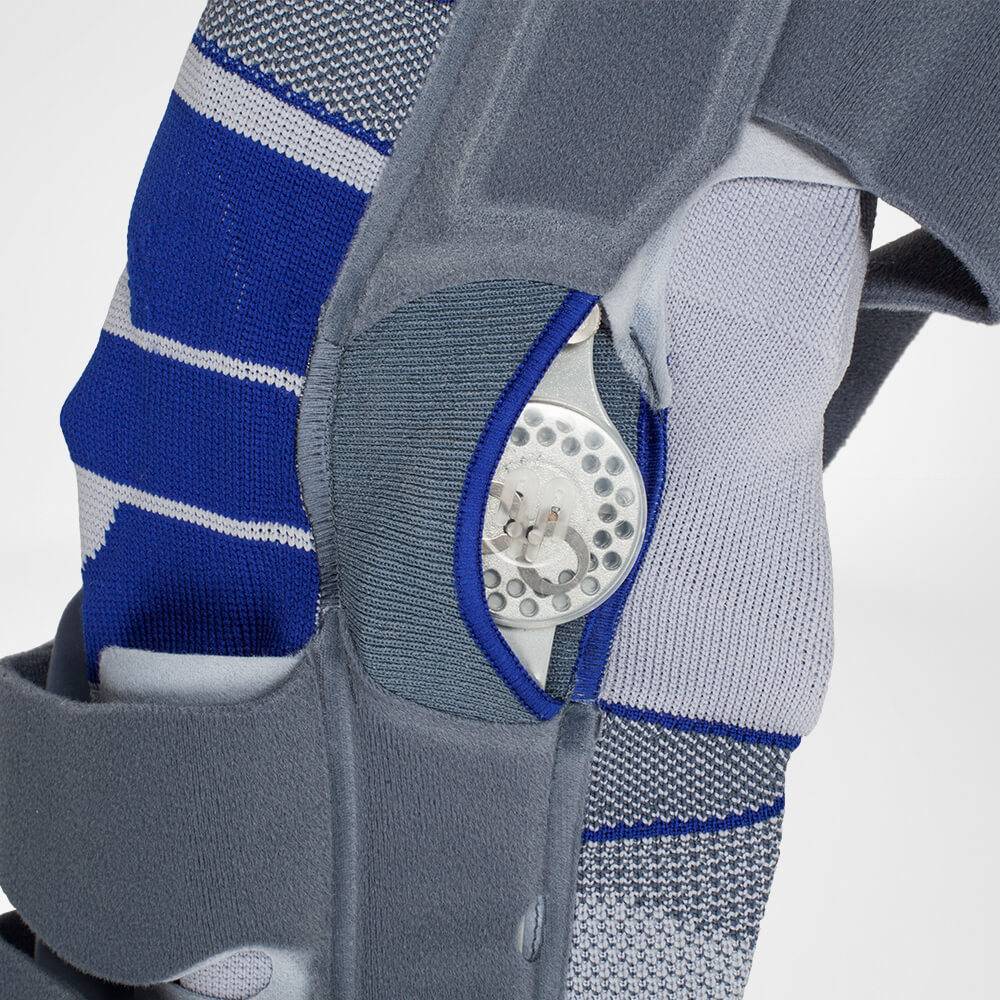
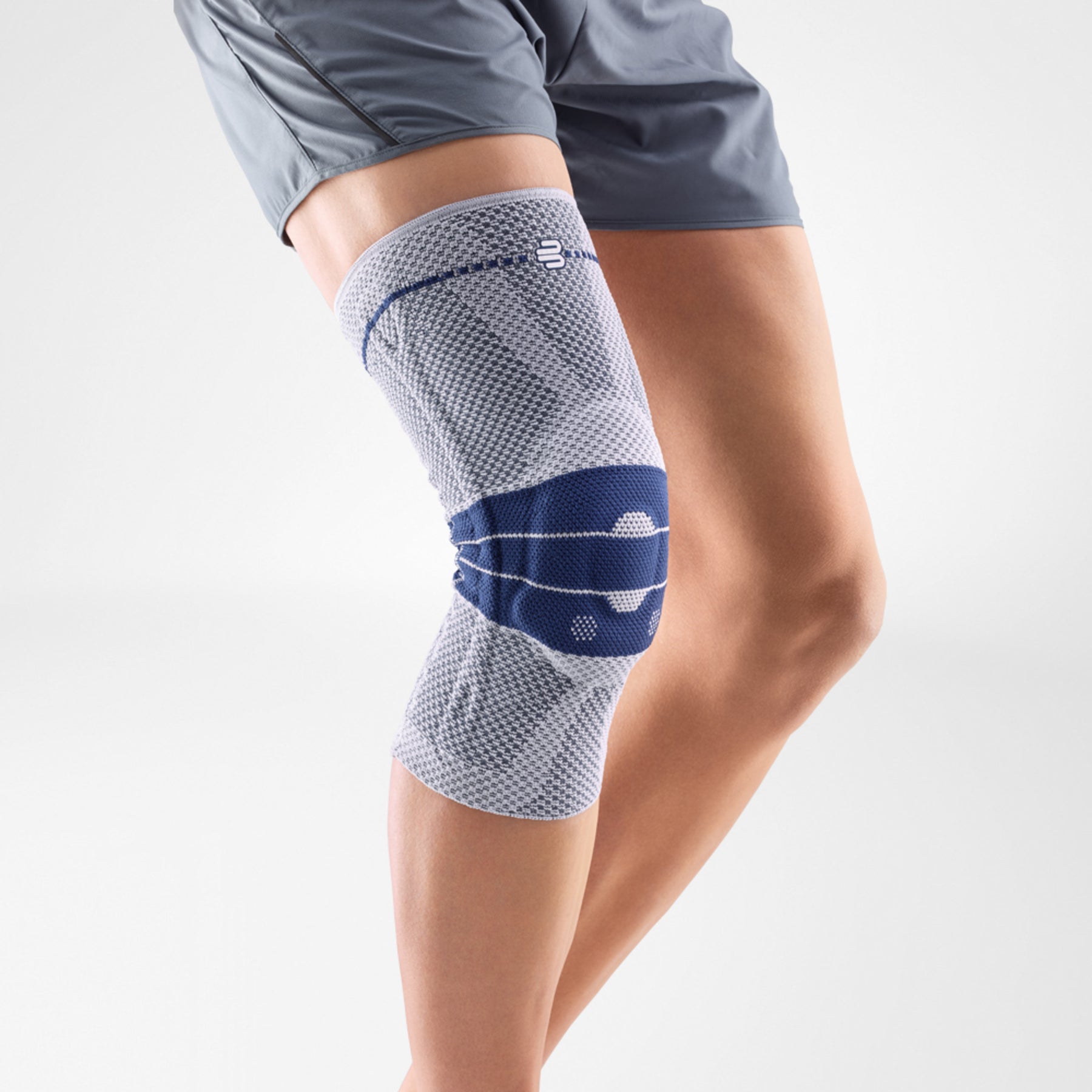
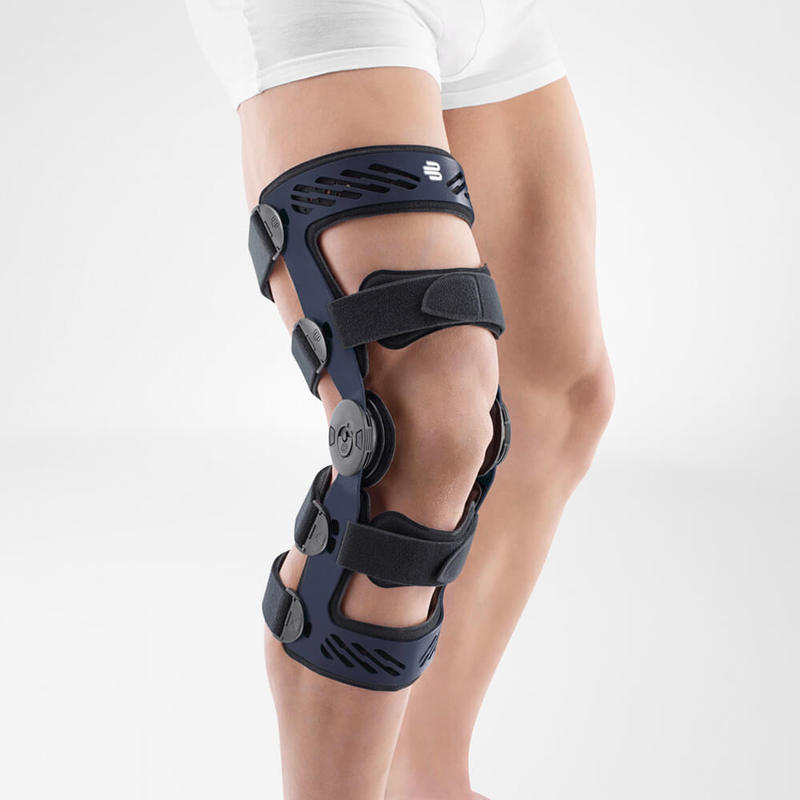
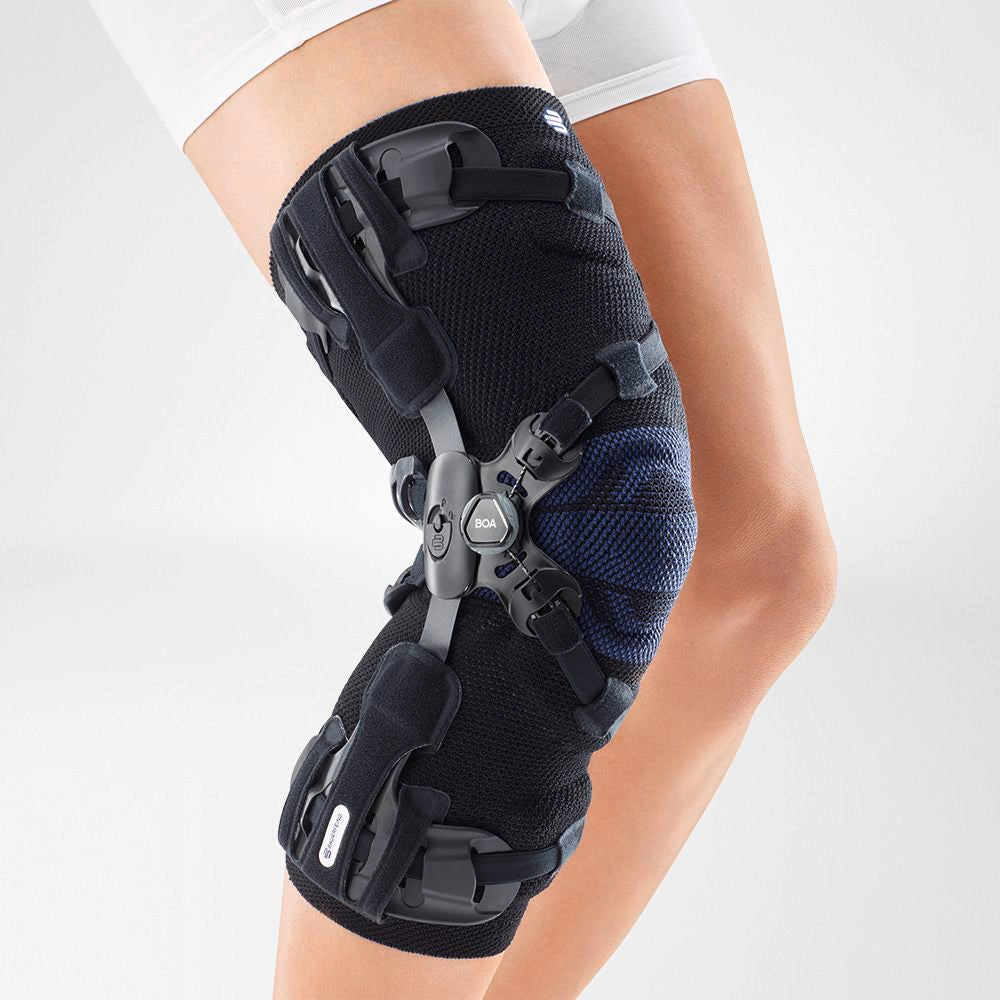
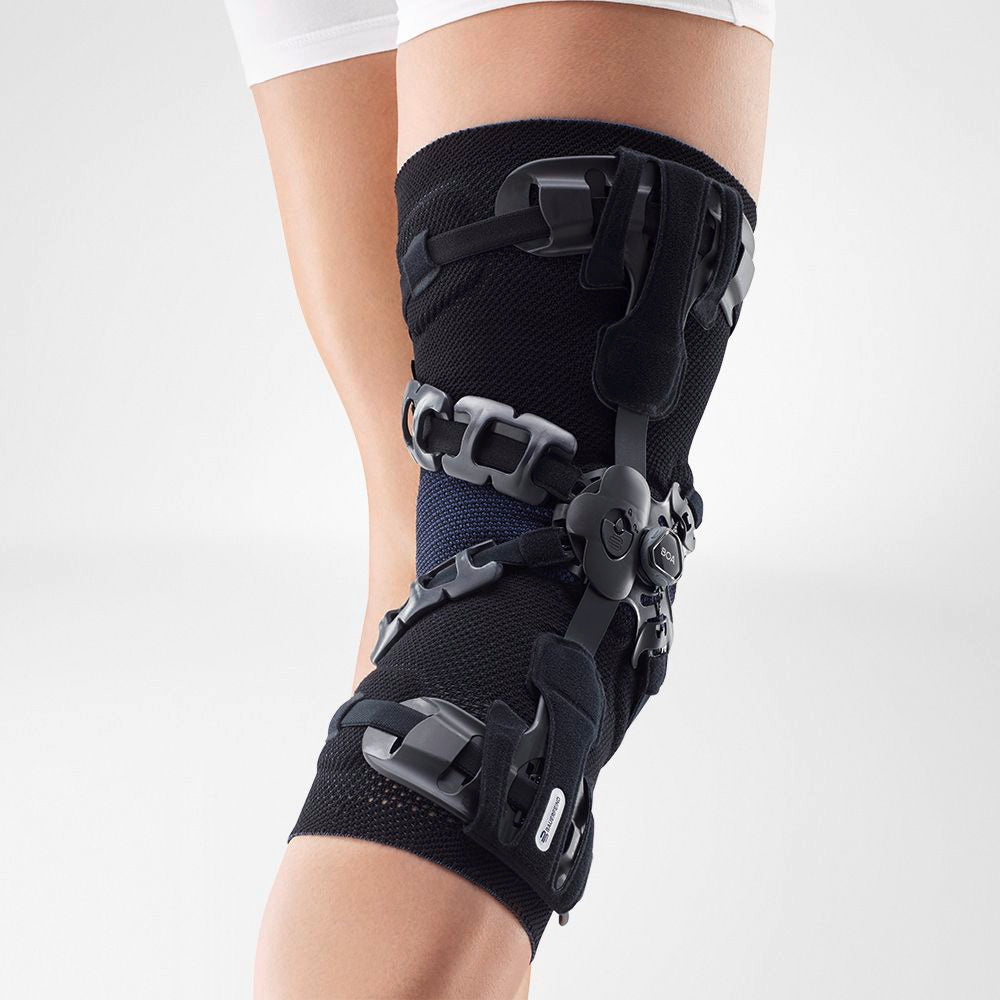
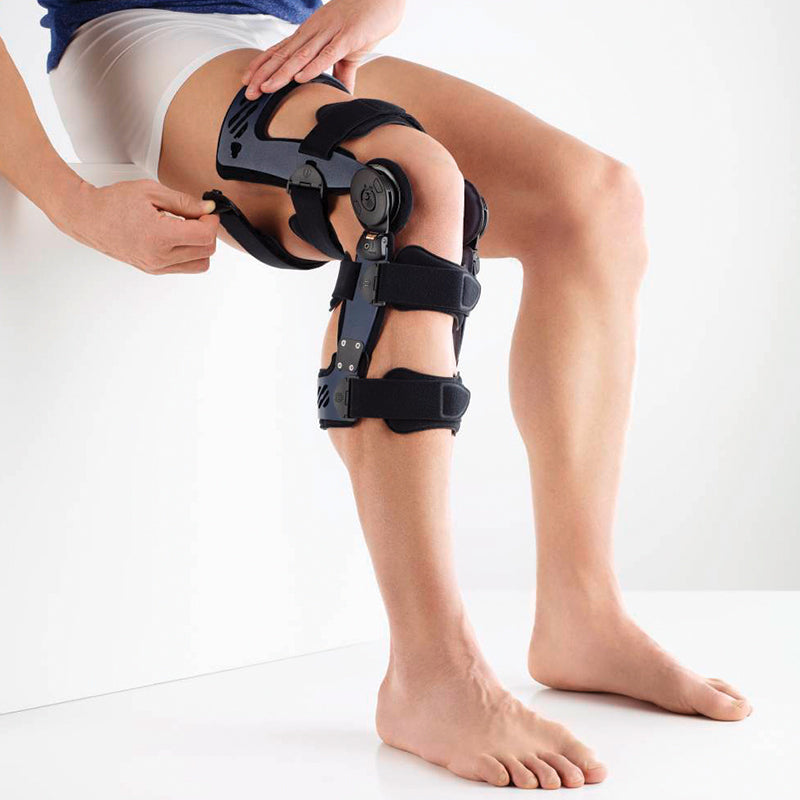
should always be combined with exercise, to promote metabolism and stimulation of the area. It is important to get mobile again as quickly as possible without causing additional pain. Using medical supports like the GenuTrain range has been shown to alleviate the symptoms and speed up recovery time.
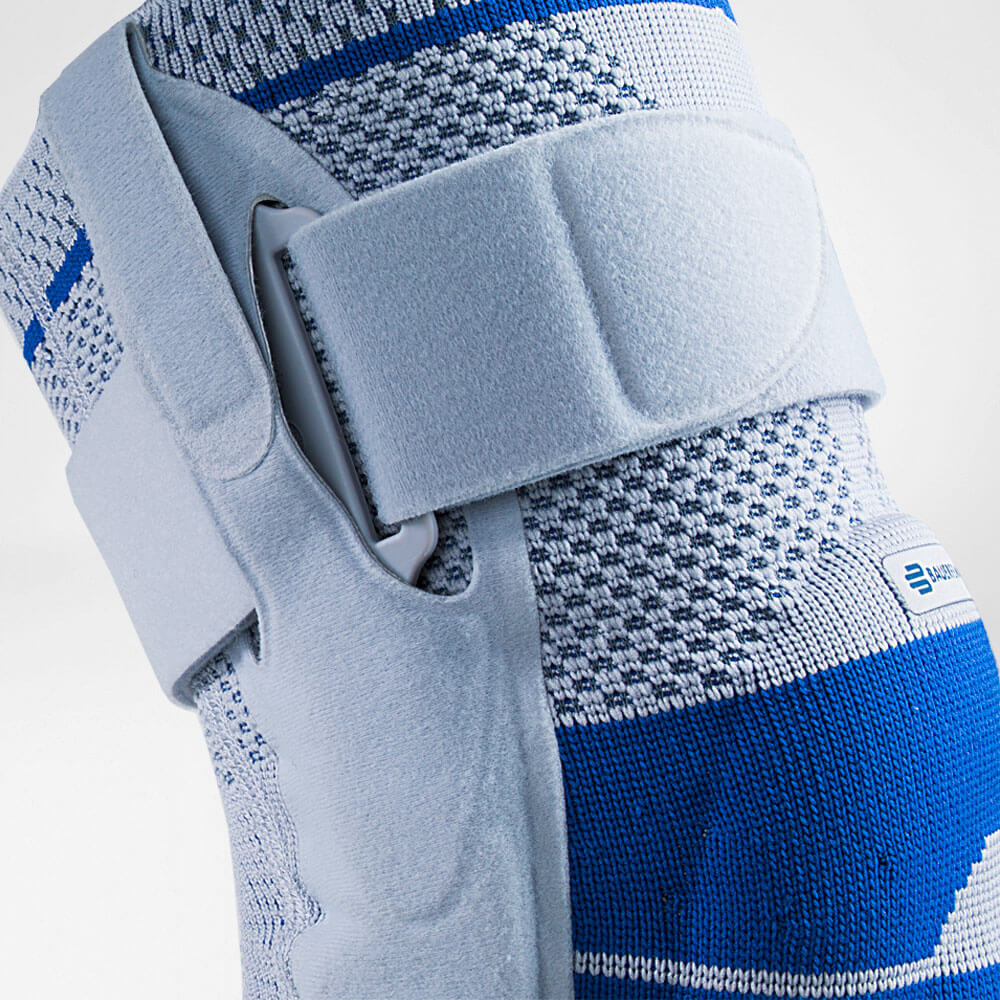
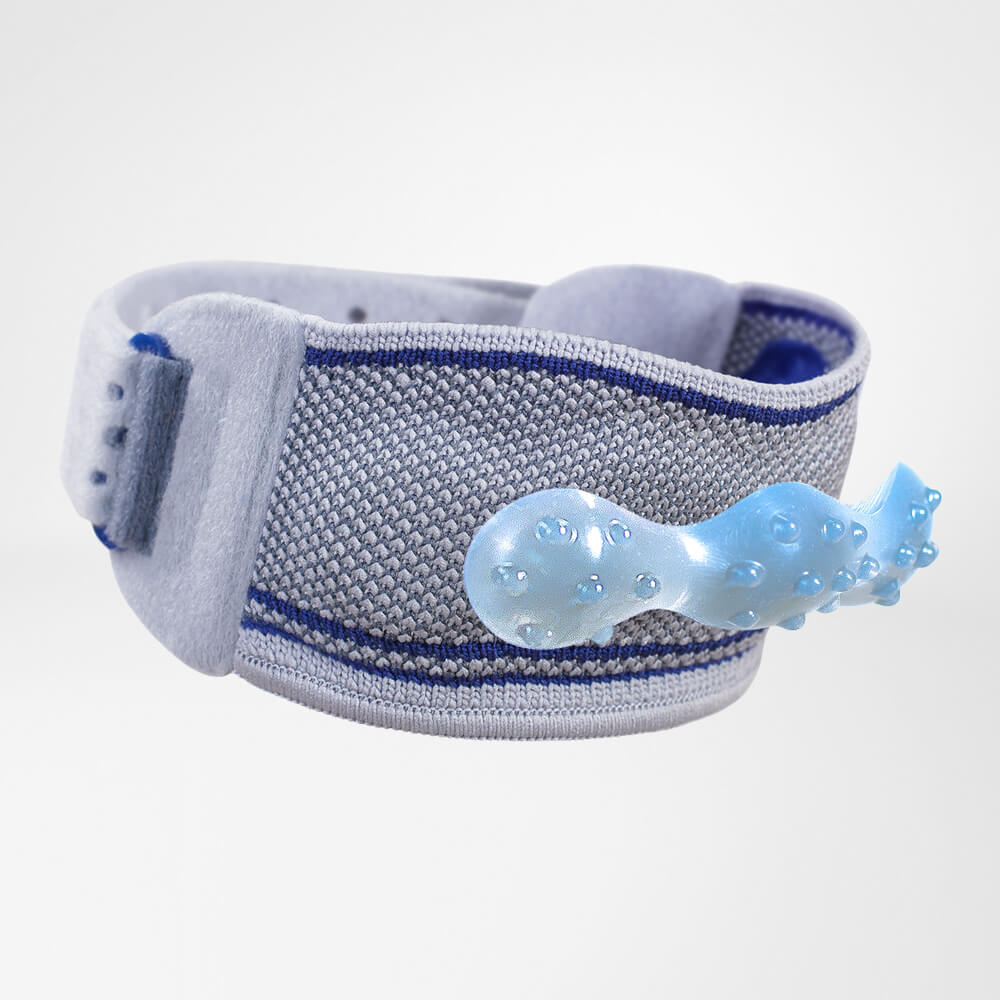
At the same time, your own proprioception of the joint is improved, which in turn stabilises the knee by activating the muscles. The anatomically shaped gel pad around the kneecap ensures there’s no painful or uncomfortable pressure on the joint, and redirects swelling into the surrounding tissue to be reabsorbed into the body.
In addition, when running, the muscles act as a pump, increasing mobility and relief from swelling. The active knit of the GenuTrain leads to external compression of the tissue. Movement then shifts soft parts, such as muscles, adipose and connective tissue. As a result, there is an interaction between external compression and movement of the soft tissue. The achieved promotion of blood circulation can accelerate the subsidence of the joint effusion in the knee.
For assistance selecting the right product for your needs, call us on +971 4 433 5684.