What is Cruciate Ligament Tear?

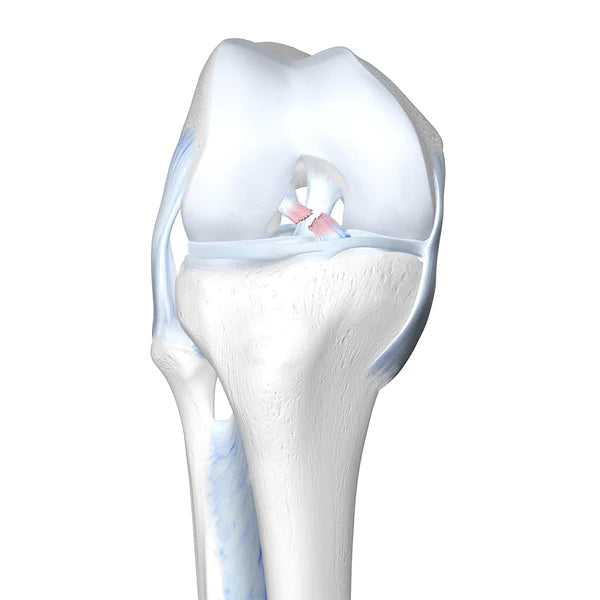
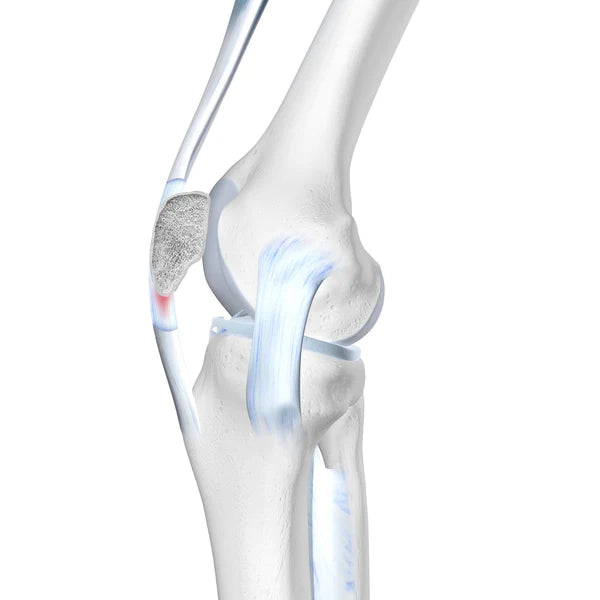
The knee joint is a complex structure that facilitates mobility and allows for complex movements including walking, running and jumping. Anatomically, the knee consists of two cruciate ligaments: Anterior and Posterior cruciate ligaments. Together they allow the knee to stretch and contract, resulting in movement. Abnormal and excessive stress can lead to a cruciate ligament tear or even a complete rupture in some cases.
Contrary to popular belief, cruciate ligament injuries are fairly common. They are commonly associated with sporting accidents which involve excessive stress and sudden shifts in direction, comparable to movements in basketball and rugby. Strong external forces, like that in a road accident, can also result in a ligament tear or rupture.
A cruciate ligament injury can be very painful and can severely restrict a patient’s mobility. It is highly recommended that immediate medical treatment be sought, as such injuries tend to have major complications.
Diagnosis and Symptoms of the Cruciate Ligament Tear

Effective diagnosis begins with determining the severity of the injury as well as narrowing down the specific area affected.
Doctors perform the “Drawer test” to determine which of the ligaments in the knee is affected. Sophisticated imaging, like the use of an MRI or X-ray, is often used to assess the injury and study a patient’s symptoms.
A cruciate ligament tear occurs when the ligaments are stretched beyond their natural range of movement.
- In this case, a clear crack can be heard and a patient’s knee will swell up almost immediately.
- Patients will experience weakness and instability in the joint as well as significant pain, which intensifies under stress.
Most mild cases can be resolved with ample rest and rehabilitation.
However, there is long term degeneration of the ligament in chronic cases. The damage will stop the joint from stretching or bending, thereby severely restricting the mobility of the individual. More drastic measures such as surgical intervention may be required in severe ligament rupture cases.
Treatment of the Cruciate Ligament Tear
Treatment of a cruciate ligament tear aims to relieve pain, stabilise the knee and restore performance and mobility of the joint. The severity of the tear (partial or complete rupture) dictates which course of treatment is carried out. Unlike other injuries, surgical intervention may be necessary depending on the severity of the injury.
Non-Surgical Treatment for ACL
Immobilisation
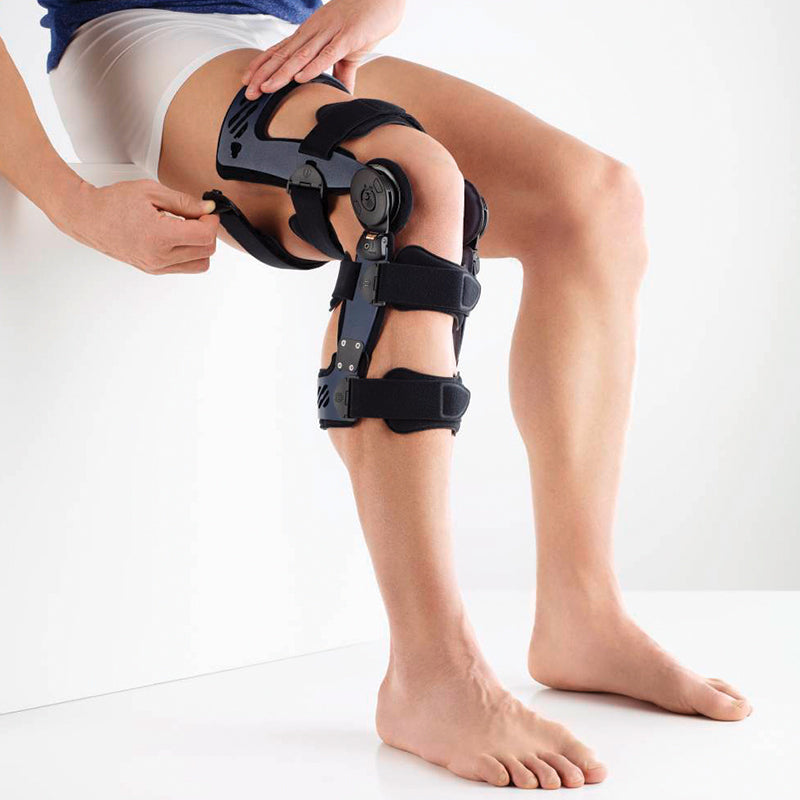
Complete immobilisation and relief from all external stress is the first step in treating a cruciate ligament injury. The ligament should be rested, and ample support should be provided, through using a medical knee brace, to restrict the movement of the joint.
Suspension of the joint is also highly recommended. Application of cooling blankets and ice packs can be very helpful in managing any swelling or inflammation caused by the injury.
*Note- Ample recovery time is recommended, even if the pain symptoms subside, to ensure complete healing. Physiotherapy should follow once the pain has subsided, in order to regain strength and mobility.
Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy
Prescribed rehabilitation, such as hydrotherapy and remedial massage, helps in boosting blood circulation and helps facilitate healing.
For example, regulated physiotherapy in the form of “targeted muscle building” has been proven to be an effective treatment path. These exercises can repair the ligament and facilitate recovery.
Prescribed Painkillers
Such as Ibuprofen or Panadol, can be used to alleviate pain and discomfort in patients. However, pain is a crucial indicator of the injury. Painkillers merely mask the pain without addressing the underlying condition.
Surgical Treatment
An operative procedure is fairly common when the anterior cruciate ligament is damaged. If a patient is physically very active, like athletes, the damaged ligament is too damaged and hence often operated on.
Surgery takes place about four to six weeks after the trauma and involves transplanting part of the patellar tendon or the hamstrings to replace the anterior cruciate ligament. It is highly recommended that patients are prescribed appropriate physiotherapy to recover effectively after surgery.
*Note: In some cases, meniscus cartilage might be damaged and are often sutured together during surgery.
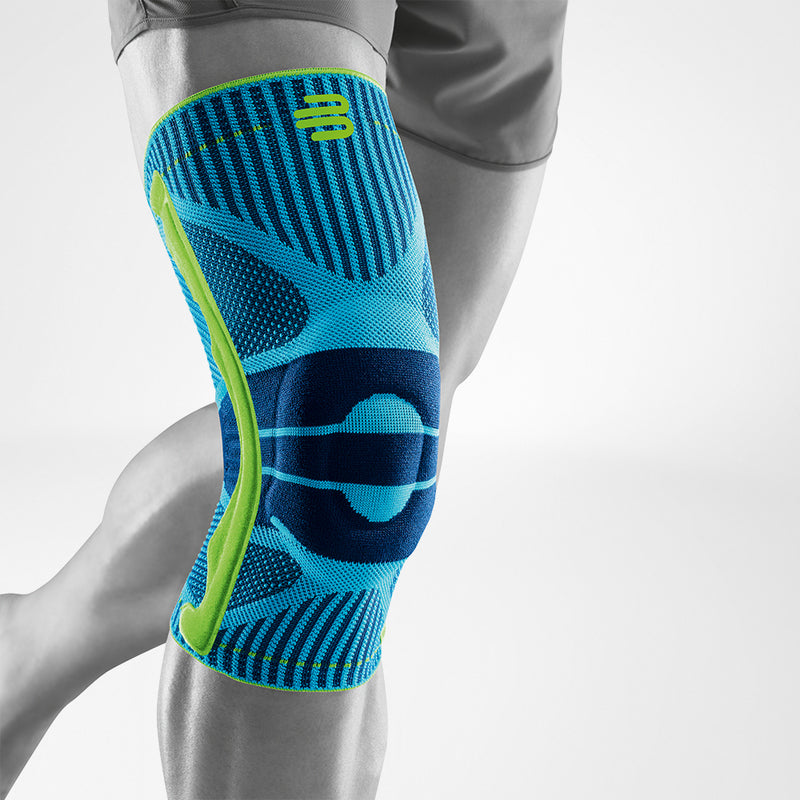
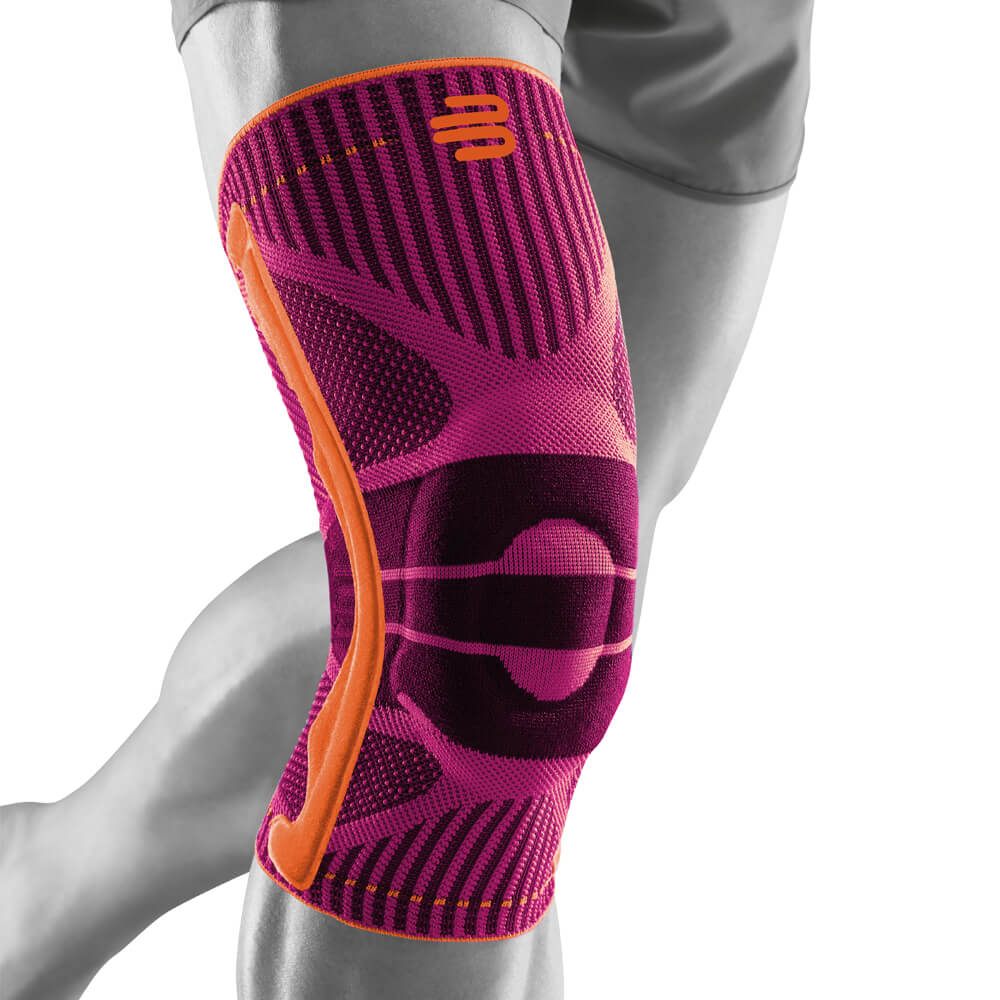
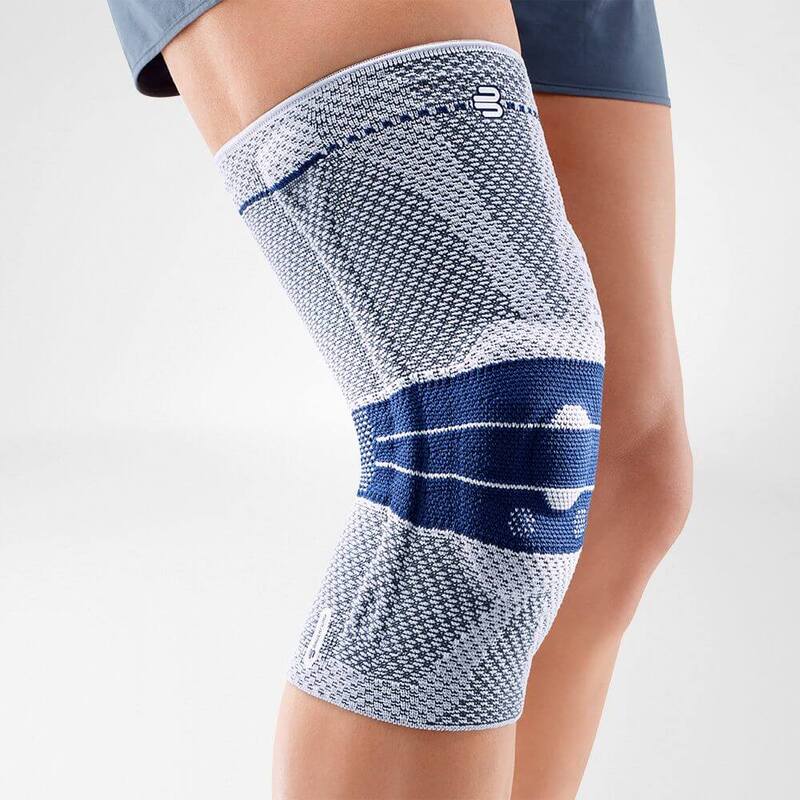
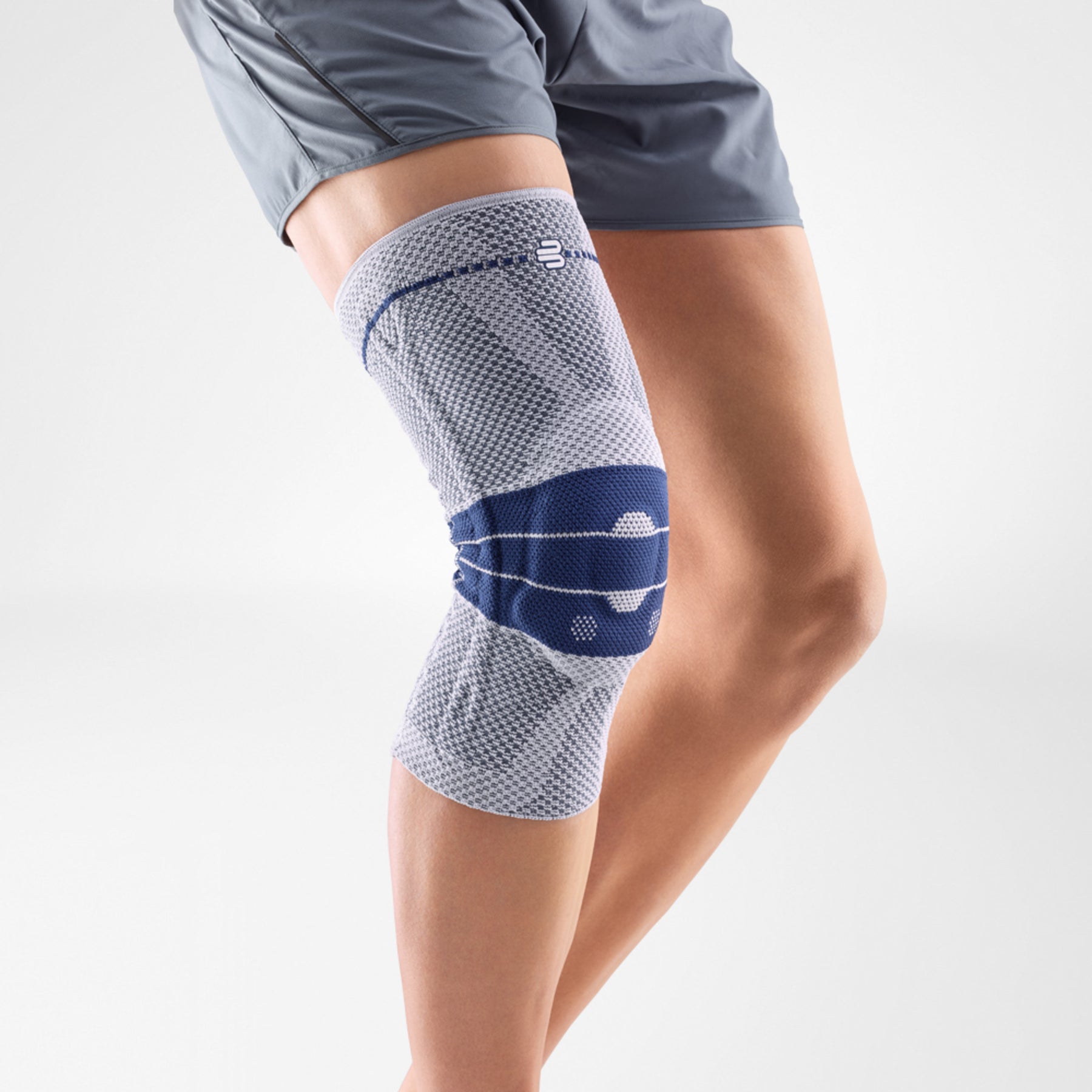
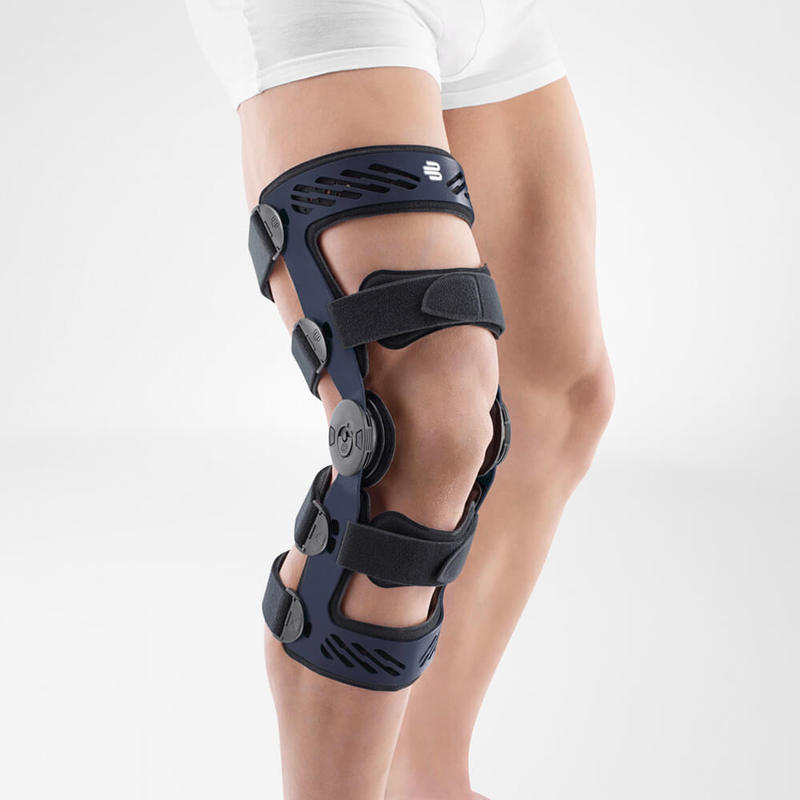
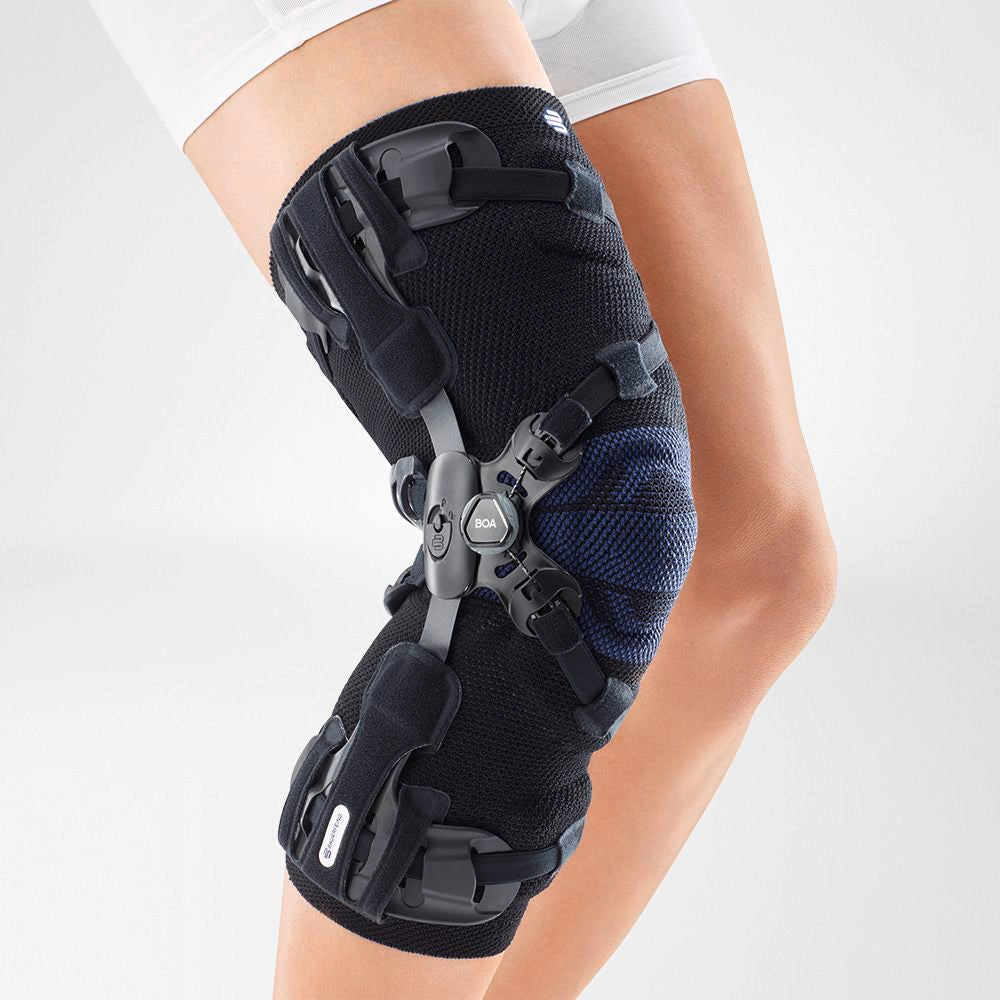
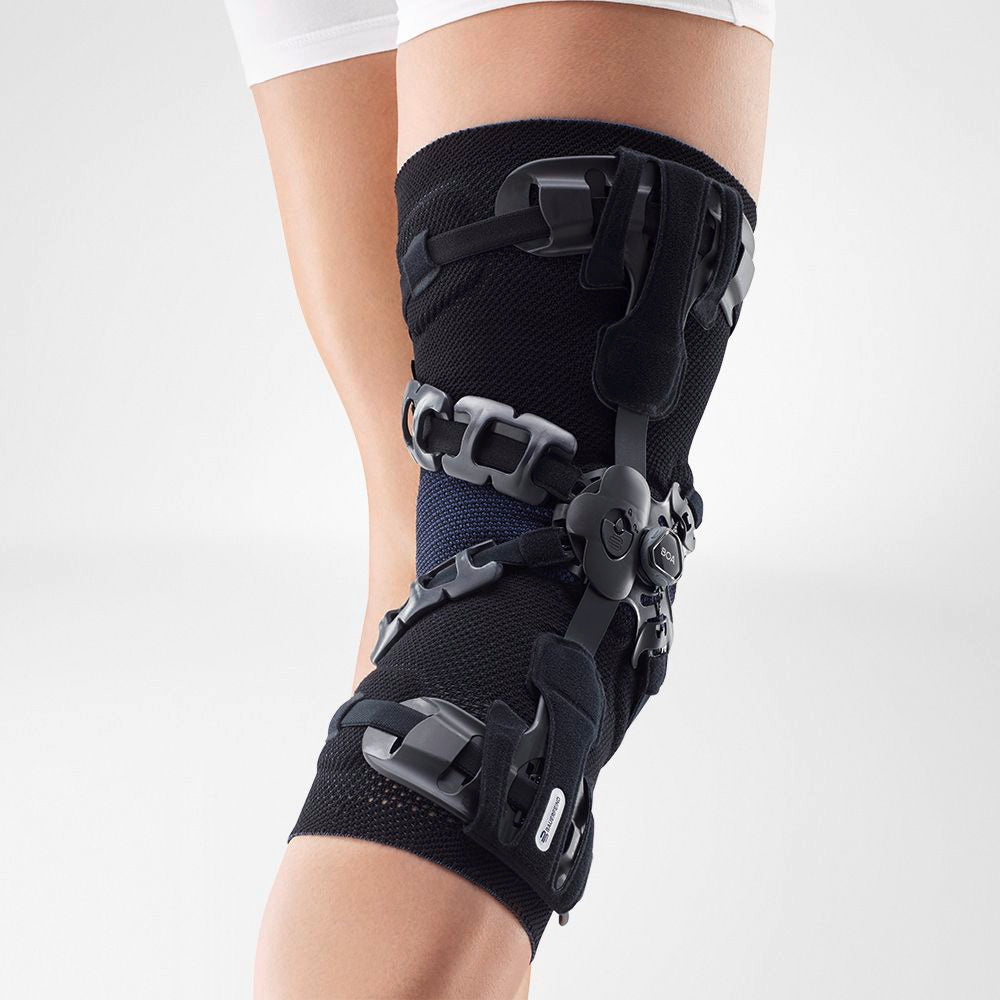
Medical Knee Braces
Medical knee braces provide crucial support and help alleviate excess pressure off the joint. Braces play a crucial role in the recovery process in both acute and post-operative procedures.
Wearing a Bauerfeind knee support can minimise your chances of further or re-injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception and medical-grade compression.
Stabilisation of the knee through Orthosis
Cruciate ligament injuries are a direct result of physical trauma due to external forces or sudden abnormal movements in succession, like in sports activities. It is crucial to understand the natural limitations of the knee joint in order to prevent the occurrence of injury.
Proper exercise technique, and the correct proprioception in itself, can help prevent excess stress on the joints and ligaments, thus reducing the chances of a cruciate ligament tear or rupture.
How do Bauerfeind medical knee braces help in treating cruciate ligament tear?

Bauerfeind’s
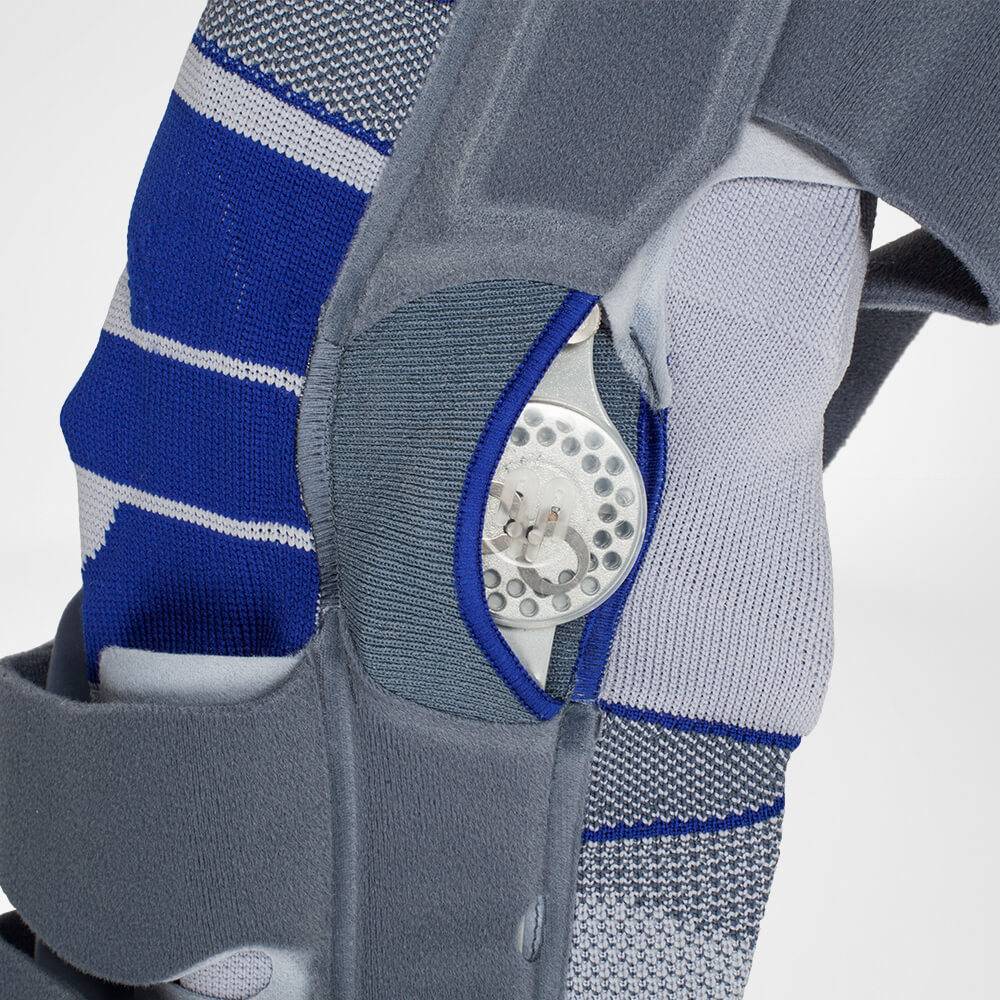
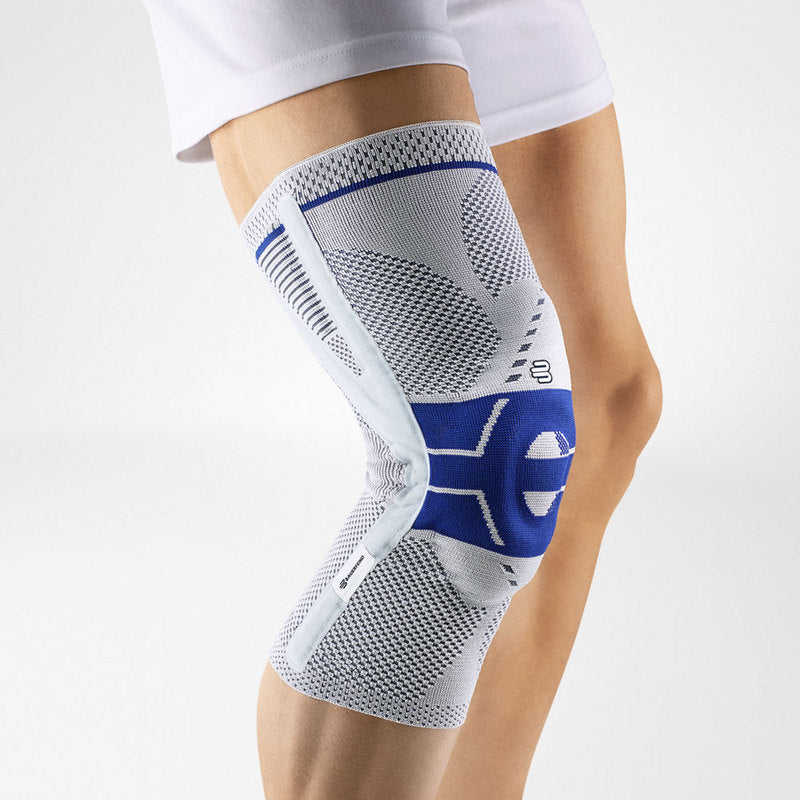
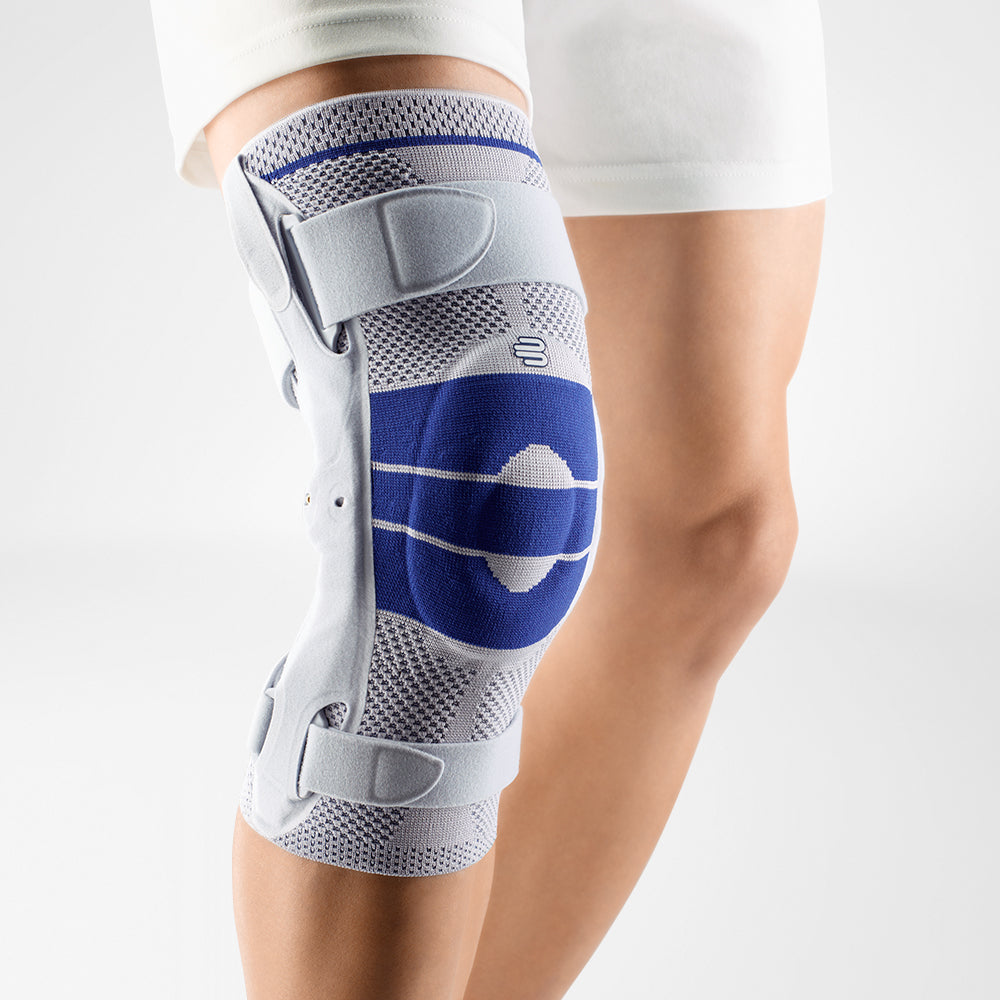
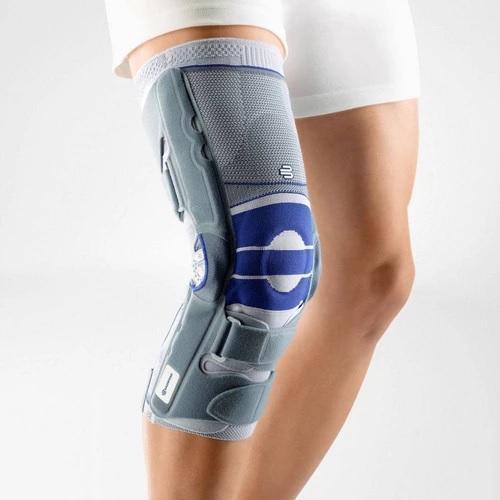
SofTec Genu is a knee brace that ultimately stabilises and unloads stress off of the knee joint without restricting your mobility.
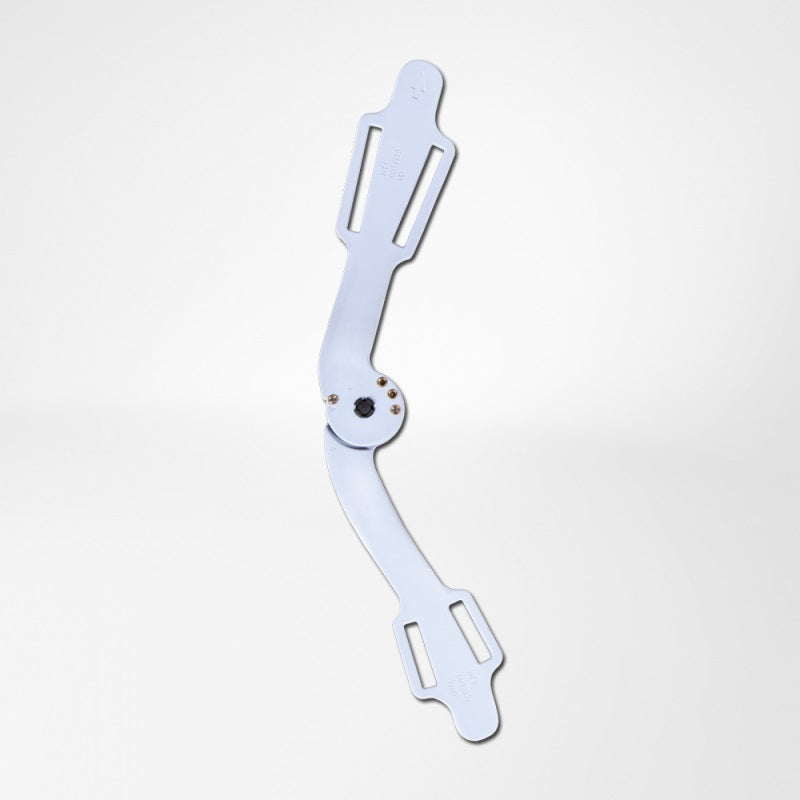
The brace features modifiable and 'intelligent' lateral and medial joints that provide optimal guidance to the knee by anatomically adjusting to each individuals axis of rotation thus minimising stress and alleviating pain.
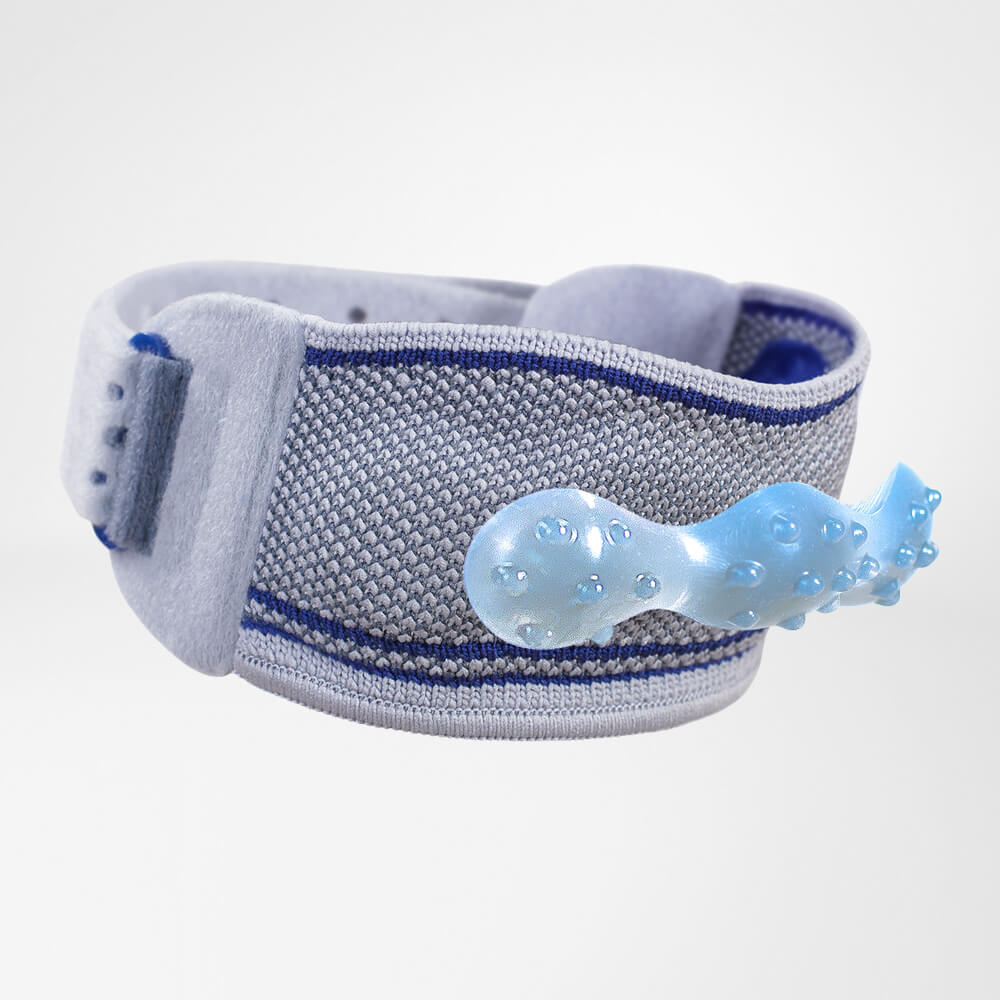
The SofTec Genu features medical-grade compression with an intertwined knee pad that has nodules built-in. Every movement activates the nodules thereby massaging the surrounding tissue, speeding up the healing process. It can also be used as an effective prevention measure (for example, it is highly effective if used while running or skiing).
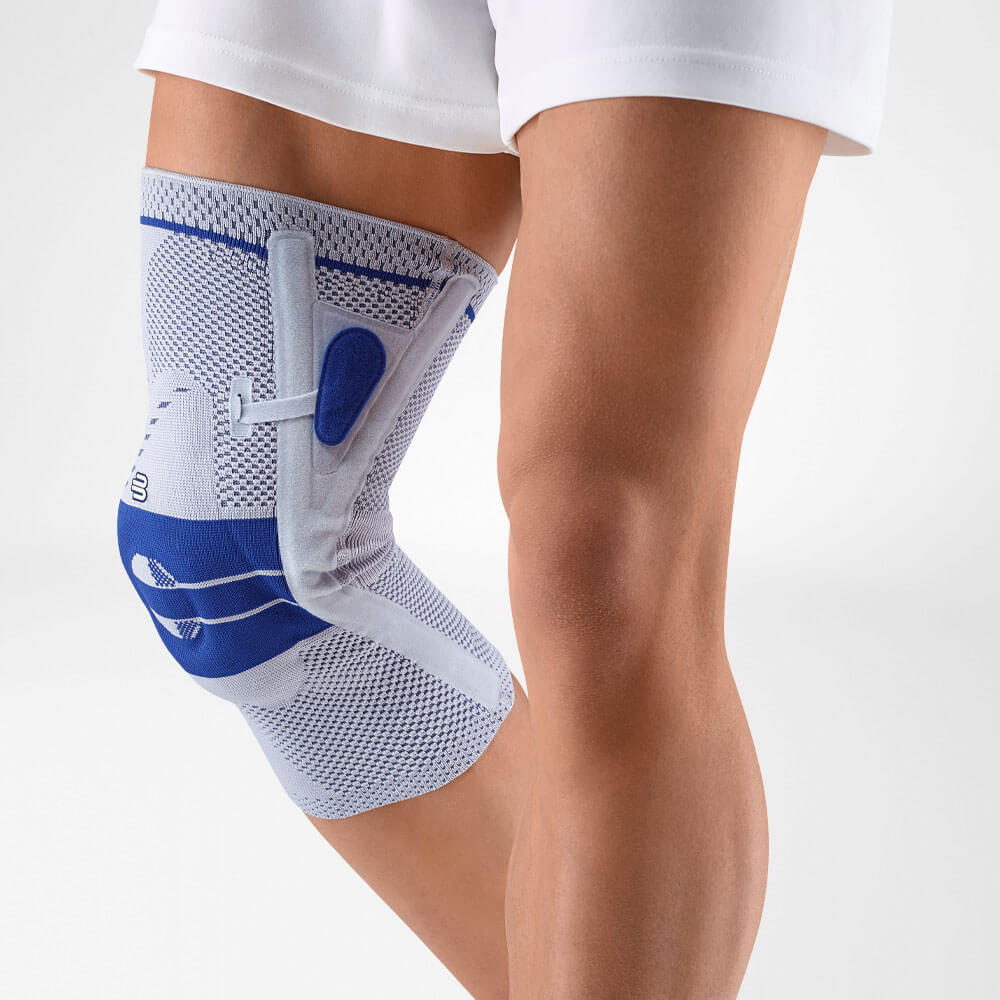
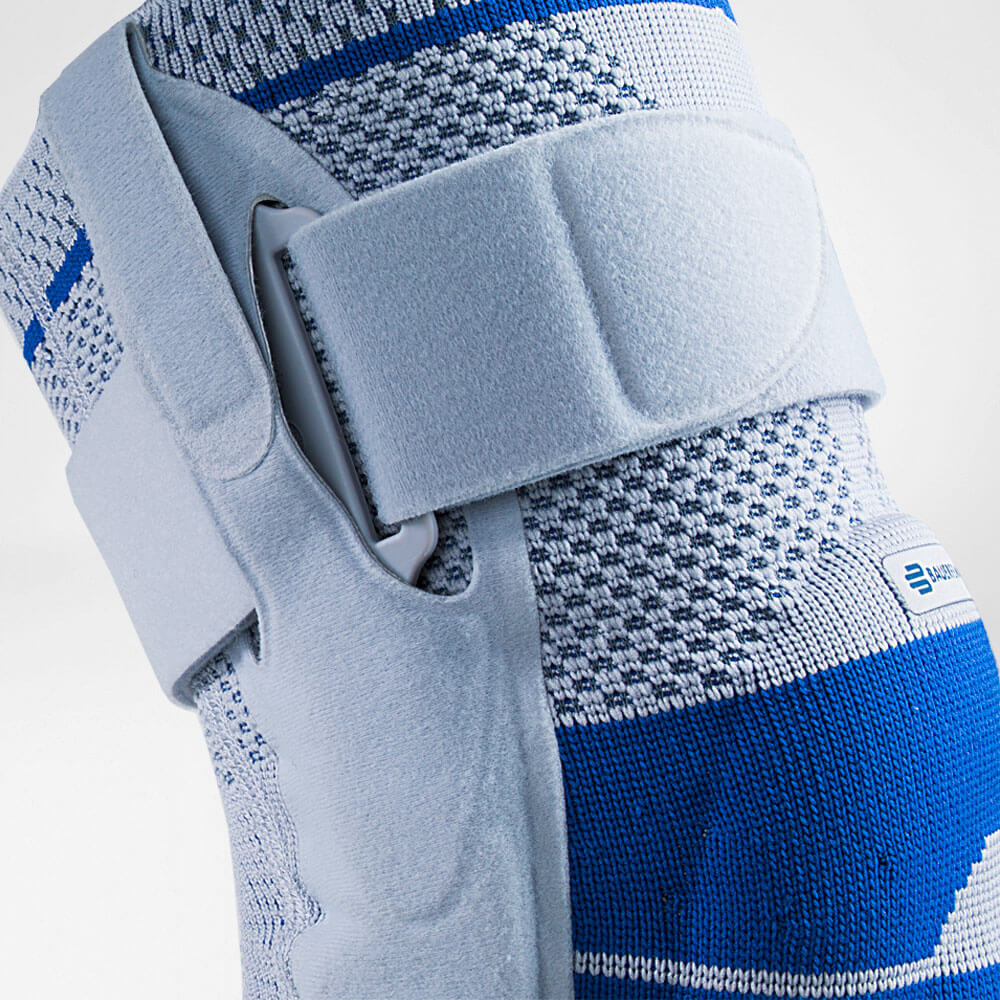
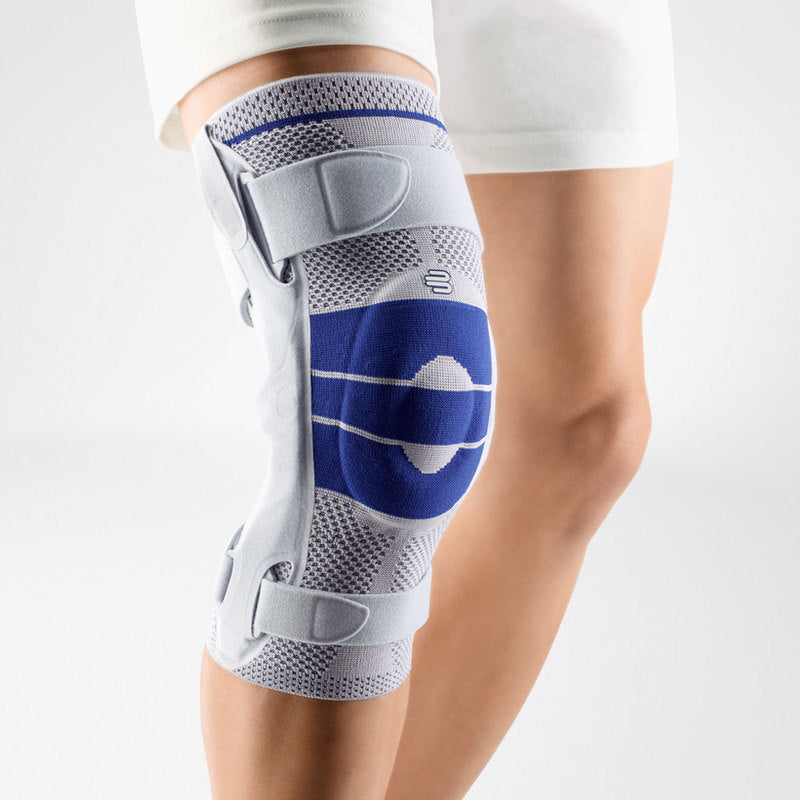
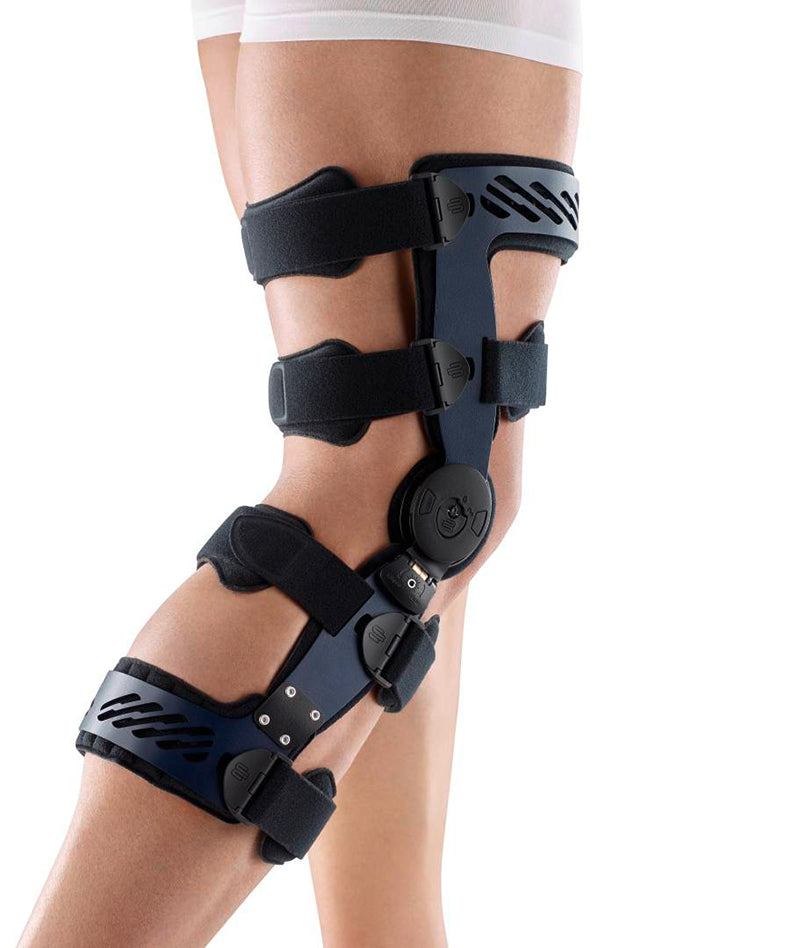
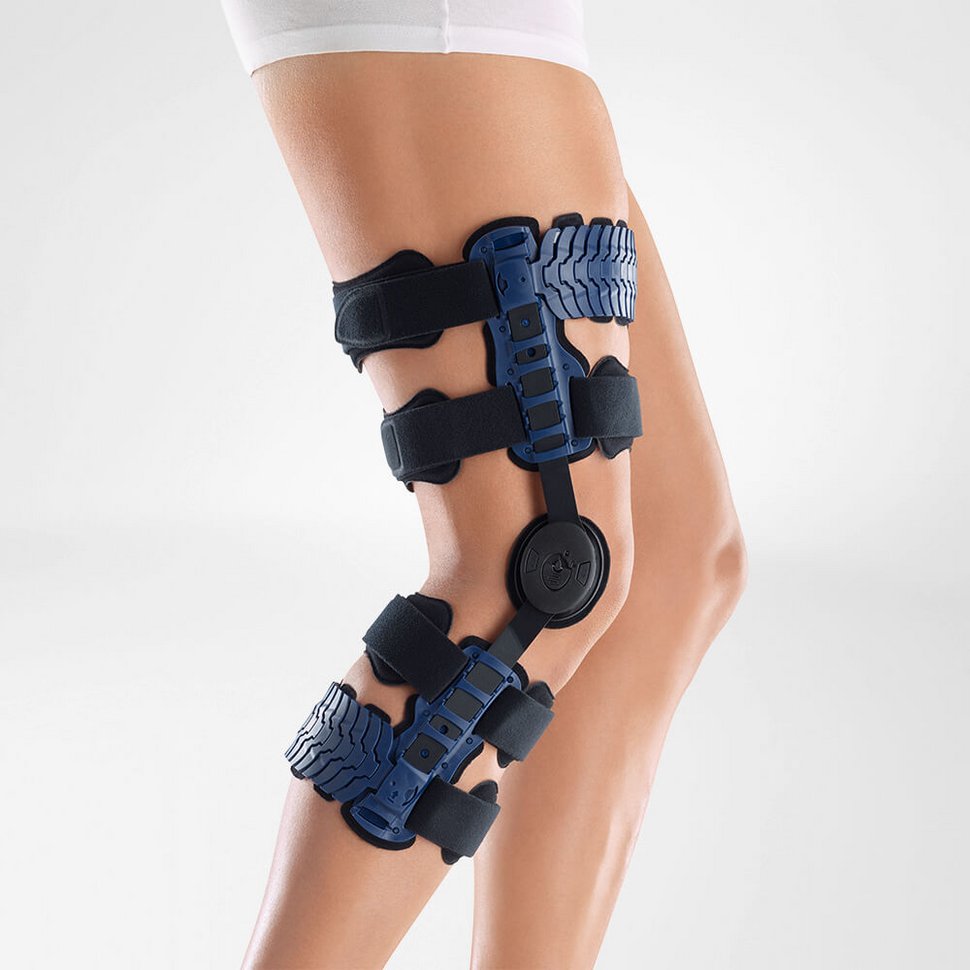
Bauerfeind’s SecuTec Genu features a hard frame which is light and durable.
The frame externally stabilises the knee joint as well as prevents unnecessary movement of the knee. This brace is suitable to be used in all stages of recovery from a cruciate ligament injury, as limitations on flexion and extension knee movements can be easily adjusted.
Medical Knee Braces, like the SecuTec Genu and SofTec Genu, play a significant role in providing ample support as well as facilitating healing from a cruciate ligament tear.
For assistance selecting the right product for your needs, call us on +971 4 433 5684.